Primed In Situ (PRINS) Labeling of RNA
互联网
521
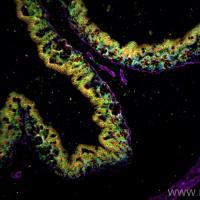
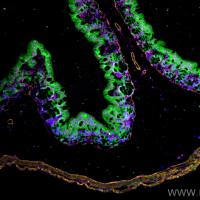
It has been possible for a number of years to detect RNA in situ in fixed cells or whole tissue-sections by the use of cloned probes (1 –4 ). The probes are labeled either with radioactive nucleotides or modified nonradioactive nucleotides, such as biotinylated dUTP, which can be visualized by fluoresceinconjugated avidin. RNA-studies by this strategy have the advantage of being very sensitive, and give a quantitative impression of the variations in RNA contents in the cells/tissue sections studied. However, it is not possible to study closely related RNA populations by these methods because the probes used are generally long and do not allow the detection of small differences, such as single base mutations or minor splicing-errors. Such a detection is made possible by the recently described “in situ transcription” (IST) method involving the direct synthesis of a first strand cDNA in situ (7 –10 ). In this method, labeling is achieved by annealing unlabeled short oligonucleotides to the target RNA and using these as primers for chain elongation in a reaction catalyzed by AMV-reverse-transcriptase in the presence of radioactive nucleotides.