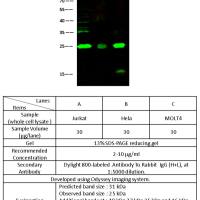
Genotyping of Mutation in the Beta-Globin Gene Using DNA Microarrays
互联网
560
Genotyping using DNA microarrays is a cost-efficient method compared with real-time PCR and DNA sequencing. Here, a DNA microarray-based method using allele-specific oligo hybridization is demonstrated. This method relies on immobilization of probes that are specific for wild-type sequences or the mutated sequences, respectively. The method makes use of agarose film-coated glass slides, unmodified DNA probes, target preparation using T7 in vitro transcription, labeling of target using biotin labels, and detection using alkaline phosphatase precipitation reaction. Visualization is performed using a desktop computer scanner. Because the biotin/strepavidin chemistry is utilized, the method described here is compatible with many different detection methods. The demonstrated colorimetric detection of mutations has an expected error frequency of about 5 � 10−7 per mutation or better. Given this low error frequency, an array diagnosing 100 different mutations would misclassify about 1 patient in 100,000.