Detection of Nitric Oxide Formation in Primary Neural Cells and Tissues
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐
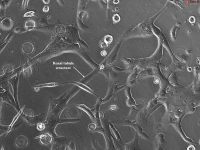
3D Renal Tubule Formation Kit
$921

Recombinant-Mouse-Epithelial-membrane-protein-3Emp3Epithelial membrane protein 3; EMP-3 Alternative name(s): Hematopoietic neural membrane protein 1; HNMP-1 Protein YMP
¥10234

3-Bromo-4-Nitropyridine N-Oxide;S70451--
¥90

MKN45人低分化胃癌细胞|MKN45细胞(Human Poorly Differentiated Gastric Cancer Cells)
¥1500

RELT/RELT蛋白Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 19L protein (RELT)重组蛋白Receptor expressed in lymphoid tissues蛋白
¥1344
相关问答

