L-Mimosine (-(3-Hydroxy-4-Pyridone-1-yl)-L-Alanine)
互联网
1645
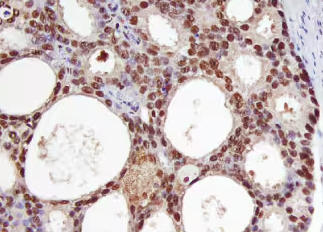
L -mimosine is a nonprotein amino acid. Despite the consideration of Leucaena leucocephala as a promising alternate source of protein for fodder, the presence of mimosine to the extent of 2% to 10% dry matter in the leaf and 2% to 5% dry matter in the seed has limited its use as a livestock feed since mimosine and its degradation products 3-hydroxy-4-(1H )-pyridone (3,4-DHP) and 2,3-dihydroxypyridine (2,3-DHP) have been known to be toxic to many species (Fig. 1) . Ingestion of mimosine results in hair loss, goiter, reproductive disorders, epithelial damage, reduced feed intake, and ultimately death in both nonruminants and ruminants. Outbreaks of human alopecia have also been reported in some areas. Certain segments of the human population are known to consume portions of the leucaena in their diet, and a loss of hair has been frequently observed among those individuals who eat the leaves, pods, and seeds in the form of a soup. Resistance to mimosine toxicity in ruminants of certain geographical areas has been attributed to the capability of their rumen microorganisms to restrictively metabolize mimosine and DHP. From the rumen of goats in Hawaii resistant to mimosine toxicity, a microorganism (Synergistes jonesii ), capable of metabolizing mimosine and DHP to innocuous products has been successfully transferred to the rumen of cattle in Australia that were susceptible to mimosine toxicity (Fig. 1 ). This gave these cattle the capability to utilize effectively the mimosine-containing forage.