相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
大量
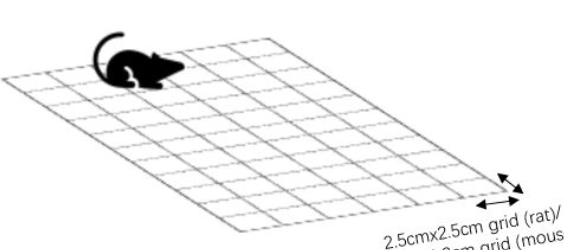
The foot-fault test, also known as grid walking test, assesses motor function and limb coordination in rodents. Basically, animals are placed on an elevated grid with square openings and allowed to move across the grid. They move around the grid by placing feet on the wire frame. If the paw falls from or slips off the frame, one foot-fault is recorded. The total number of steps it takes to cross the grid and the foot fault for each limb are quantified. Sham controls have few foot faults with no bias toward either side, while mice with stroke display increased foot-faults toward the contralateral side. To reduce individual variation, a pre-stroke test should be performed to customize the post-stroke result.
The foot-fault test has been used to study limb coordination in ischemic stroke. Short-term studies revealed that mice made significantly more foot-faults at day 2 after MCAO compared to sham controls, indicating acute coordination deficits. The coordination deficits can be observed up to 90 days after stroke. Compared to wildtype controls, mice with attenuated astrocyte reactivity displayed substantially more foot-faults up to 4 weeks after MCAO, indicating slower recovery.64 Similarly, the foot-fault test is also able to detect short-term and long-term deficits in ischemic rats. It was reported that increased foot-faults were observed in rats at days 2-28 after MCAO. In addition, rats exhibited increased foot faults in a hypoxia–ischemia model and the motor coordination deficits could still be detected 5 weeks after surgery. These findings suggest that the foot-fault test is sensitive enough to detect both short-term and long-term motor coordination deficits in ischemic stroke.
The foot-fault test has also been used to detect limbs deficits in hemorrhagic stroke. Increased foot-faults were observed in mice at days 3 and 7 after ICH, indicating shortterm coordination impairment. Similar results were reported in ICH mice 2 and 3 weeks after stroke, indicating long-term coordination deficits. Like mice, rats also displayed limb deficits at both acute (day 1) and chronic (day 21) phases after ICH. In addition, rats also showed increased foot-faults 2 weeks after SAH. These results suggest that the foot-fault test is also useful in the assessment of motor coordination deficits in hemorrhagic stroke.
The foot-fault test is effective and objective in assessing motor function and limb coordination. Similarly, it can also evaluate long-term stroke outcome in both ischemic and hemorrhagic models.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验Neurobehavioral Assessments of Neonatal HypoxiaIschemia
(righting reflex, negative geotaxis, and gait) and an early motor coordination test (grid walking and foot-fault test), as well as the required materials and tools to perform such assessments.
作者:赵晴 昆明市东川区人民医院检验科 肥达反应(Widal test): 用已知伤寒、副伤寒沙门菌的O、H抗原,检测受检血清中有无相应抗体的半定量凝集试验,称肥达反应(Widal test)。本试验与细菌分离培养同时进行或在前者失败的情况下,能辅助诊断伤寒、甲、乙、丙型副伤寒沙门菌引起的肠热症。 外斐反应(Wiel-Felix): 斑疹伤寒等立克次体与变形杆菌某些X株的菌体抗原(OXk、OX19 、OX2抗原)具有共同的耐热性多糖类属抗原,常用后者代替相应的立克次体抗原进行
假设检验的基本步骤 上述抽样模拟试验表明,从同一总体中以固定n随机抽样,由于抽样误差的影响,样本均数x与总体均数μ往往不相等,且两个样本均数x1和x2也往往不相等。因此在实际工作中遇到样本均数与总体均数间或样本均数与样本均数间不相等时,要考虑两种可能:①由于抽样误差所致;②两者来自不同总体。如何作出判断?统计上是通过假设检验(hypothesis testing),又称显著性检验(significance test),来回答这个问题。 下面以样本
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料