相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
大量
- 现货状态:
有

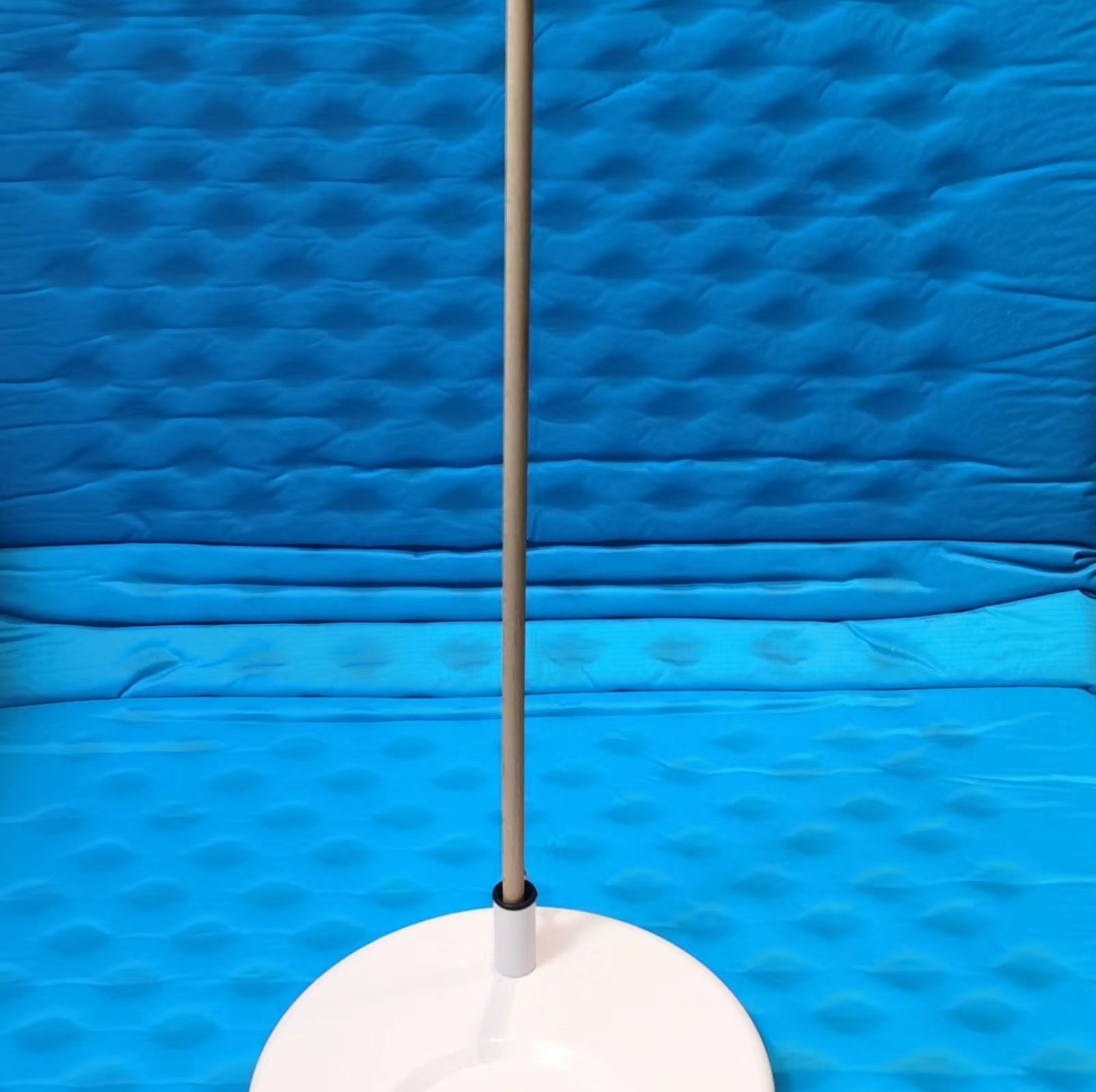
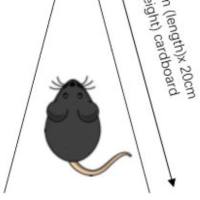
The pole test is an easy test to assess the overall locomotor function in rodents. It was initially developed on mice to study bradykinesia and later adapted to stroke studies. Although the pole test has been used in rats for other studies, it is seldom used in rat stroke models. This is possibly because rats are heavier than mice, which makes them unable to perform the task after stroke. In this test, a mouse is placed on the tip of an 8mm (diameter) x 50cm (length) wooden pole with its head upward. The mouse then tries to descend to the floor by turning its head downward. The latency to make the turn (Tturn) and the time to descend (TD) are recorded. For mice that descend without turning their heads downward, the TD is used to represent Tturn. If mice make the turn but fall in the halfway when descending, the total time until they reach the floor is recorded. If mice fall immediately, the maximum duration of 120s is assigned to the Tturn and TD. It should be noted that mice cannot pause during descending. If this happens, the trial should be excluded and repeated. For better performance, mice need to be trained before stroke induction.
The pole test is a useful assessment of locomotor function in ischemic stroke. It was reported that ischemic mice showed increased T turn and TD compared to sham controls up to 11 days after injury, suggesting locomotor impairment. By day 17 after stroke, however, similar Tturn and TD were observed in sham and ischemic mice, indicating recovery. In addition, fluoxetine was able to improve animal performance in the pole test at days 12 and 20 after stroke,57 suggesting that the pole test can be used to assess neuroprotective effects of novel treatments.
In addition, the pole test has also been applied in hemorrhagic stroke. In an autologous blood-induced ICH model, mice spent more time descending compared to sham controls at day 2 after stroke, and dexmedetomidine treatment significantly improved their performance.58 In contrast, another study showed that mice failed to exhibit locomotor deficits in the pole test at days 2-7 after collagenase-induced ICH. These controversial results might be caused by different ICH protocols. In SAH models, however, the pole test is seldom performed.
The pole test is relatively easy to perform and requires minimal equipment. It is an objective and sensitive test for motor function. Furthermore, the pole test is also able to assess long[1]term motor function in ischemic stroke.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验【实验目的】 1. 了解爬杆回避实验(pole-jump test)原理。 2. 掌握爬杆回避实验方法。 【实验原理】 以灯光(和/或声音)和电击为联合刺激,使实验动物由被动回避到建立主动的条件反射。记录此条件反射建立过程中的主动回避反应指标可反应实验动物的学习、记忆能力的变化。 【实验对象】 成年小鼠,大鼠。 【实验器材】 爬杆实验装置为25cm×25cm×40cm的实验箱,箱底铺有电栅,可以通电,箱中央树立一根直径
【实验目的】 1. 了解爬杆回避实验(pole-jump test)原理。 2. 掌握爬杆回避实验方法。 【实验原理】 以灯光(和/或声音)和电击为联合刺激,使实验动物由被动回避到建立主动的条件反射。记录此条件反射建立过程中的主动回避反应指标可反应实验动物的学习、记忆能力的变化。 【实验对象】 成年小鼠,大鼠。 【实验器材】 爬杆实验装置为25cm×25cm×40cm的实验箱,箱底铺有电栅,可以通电,箱中央树立一根直径约2.5cm的木杆
Mice Models for the Manic Pole of Bipolar Disorder
a protocol for assessing spontaneous activity (see Protocol 1), since this test is critical for the interpretation of results from the other tests. It is suggested that these tests can be used independently for the study of different domains of the manic pole
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料