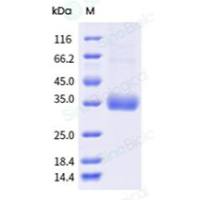
Random Fragment Libraries Using Yeast Expression Plasmid
互联网
445
The natural immune response against pathogens can be extremely varied, ranging from a strong, broad humoral and cellular response capable of stopping disease progression to a weak, inadequate, or even deleterious response inefficient at controlling replication of the infectious agent. Epitope mapping provides one approach to the understanding of the interactions between the host immune system and the attacking pathogen. Current methods for epitope mapping rely on computer models, the use of chemically synthesized peptides (1 ,2 ), and/or the development of expression assays in prokaryotic or eukaryotic environments (3 ). The former approaches can be limited, since choice of sequences synthesized or of the chemistry involved may be inappropriate to allow for proper mimicry of native determinants. The latter usually involves an immunoscreening approach to clone isolation leading to the identification of the epitope sequences.