Example of Use of TaqMan Real‐Time RT‐PCR to Analyze Bacterial Gene Transcript Levels: Haemophilus influenzae
互联网
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- Materials
- Figures
- Literature Cited
Abstract
The protocol in this unit describes the steps for gene expression analysis of Haemophilus influenzae in broth culture. Steps for hot acid phenol RNA extraction, RNA cleanup, quantitation, assessment, and preparation for TaqMan qRT?PCR are described. The validation, setup, and analysis of TaqMan qRT?PCR experiments are discussed. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 15:1D.1.1?1D.1.13. © 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: quantitative reverse transcriptase?PCR (qRT?PCR); TaqMan; RNA; gene expression; Haemophilus influenzae
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Basic Protocol 1: RNA Extraction from Haemophilus influenzae Cultures
- Basic Protocol 2: RNA Cleanup and Assessment
- Basic Protocol 3: TaqMan qRT‐PCR
- Reagents and Solutions
- Commentary
- Literature Cited
- Figures
Materials
Basic Protocol 1: RNA Extraction from Haemophilus influenzae Cultures
Materials
Basic Protocol 2: RNA Cleanup and Assessment
Materials
Basic Protocol 3: TaqMan qRT‐PCR
Materials
|
Figures
-

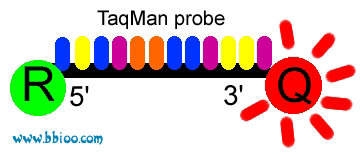
Figure 1.D0.1 Schematic of the TaqMan assay. Assays consist of primers and a probe. The probe is constructed with a fluorescent dye (reporter, R) at the 5′ end and a quencher (Q) at the 3′ end. Degradation of the probe annealed to its specific target by the polymerase separates the reporter from the quencher, resulting in a net increase in fluorescence that can be measured after each cycle. View Image
Videos
Literature Cited
| Literature Cited | |
| Fleischmann, R.D., Adams, M.D., White, O., Clay ton, R.A., Kirkness, E.F., Kerlavage, A.R., Bult, C.J., Tomb, J.F., Dougherty, B.A., Merrick, J.M., McKenney, K., Sutton, G., FitzHugh, W., Fields, C., Gocayne, J.D., Scott, J., Shirley, R., Liu, L., Glodek, A., Kelley, J.M., Weidman, J.F., Phillips, C.A., Spriggs, T., Hedblom, E., Cotton, M.D., Utterback, T.R., Manna, M.C., Nguyen, D.T., Saudek, D.M., Brandon, R.C., Fine, L.D., Fritchman, J.L., Fuhrmann, J.L., Geoghagen, N.S.M., Gnehm, C.L., McDonald, L.A., Small, K.V., Fraser, C.M., Smith, H.O., and Venter, J.C. 1995. Whole‐genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science 269:496‐512. | |
| Harrison, A., Dyer, D.W., Gillaspy, A., Ray, W.C., Mungur, R., Carson, M.B., Zhong, H., Gip son, J., Gipson, M., Johnson, L.S., Lewis, L., Bakaletz, L.O., and Munson, R.S. Jr. 2005. Genomic sequence of an otitis media isolate of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae: Comparative study with H. influenzae serotype d, strain KW20. J. Bacteriol. 187:4627‐4636. | |
| Heid, C.A., Stevens, J., Livak, K.J., and Williams, P.M. 1996. Real time quantitative PCR. Gen. Res. 6:986‐994. | |
| Kaplan, B., Wandstrat, T.L., and Cunningham, J.R. 1997. Overall cost in the treatment of otitis media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 16:S9‐S11. | |
| Livak, K.J. and Schmittgen, T.D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real‐time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402‐408. | |
| Murphy, T.F. and Apicella, M.A. 1987. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: A review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human response to infection. Rev. Infect. Dis. 9:1‐15. | |
| Smith‐Vaughan, H.C., Sriprakash, K.S., Leach, A.J, Mathews, J.D., and Kemp, D.J. 1998. Low genetic diversity of Haemophilus influenzae type b compared to nonencapsulated H. influenzae in a population in which H. influenzae is highly endemic. Infect. Immun. 66:3403‐3409. |