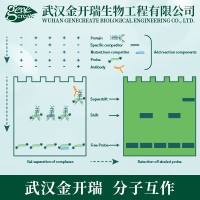
凝胶迁移滞后实验(electrophoretic mobility shift assays,EMSA)基本原理
互联网
凝胶迁移滞后实验(electrophoretic mobility shift assays,EMSA)是近年发展起来的研究核酸与蛋白质相互作用简单、快速、敏感的方法。目前已经成为转录因子研究的经典方法。
其基本原理是蛋白质可以与末端标记的核酸探针结合,电泳时这种复合物比无蛋白结合的探针在凝胶中泳动的速度慢,即表现为相对滞后(如下图所示)。该方法可用于检测DNA结合蛋白、RNA结合蛋白,并可通过加入特异性的抗体(supershift)来检测特定的蛋白质,并可进行未知蛋白的鉴定。
简单说明以下EMSA技术的优缺点,基本原理和实验方法。
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
Introduction
Advantage:
can separate different types of complexes, such as monomer and dimer => better than filter binding
easier to see the complex than footprint assay
Disadvantage: do not know where the binding site is.
Rationale
DNA-protein complex will have a smaller mobility than that of free DNA on native gel
gel electrophoresis and molecular sieve
cage effect - difference between footprint and EMSA
Data interpretation
nonspecific binding
smearing between DNA and complex bands
Methods
Lable DNA
Mix DNA and protein to form complex
Add nonspecific competitor
Separate complex with free probe on a native gel