Hyperspectral Imaging of FRET-Based cGMP Probes
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Roche 4887301001 LightCycler 480 Probes Master 10x 5ml 探针法实时定量试剂盒
¥13200

Cathepsin D and E FRET Substrate acetate,839730-93-7,≥98%,阿拉丁
¥1149.90

SIRPA/SIRPA蛋白Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 (SIRPA)重组蛋白Brain Ig-like molecule with tyrosine-based activation motifs蛋白
¥1344

Pde9a/Pde9a蛋白Recombinant Mouse High affinity cGMP-specific 3,5-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A (Pde9a)重组蛋白/蛋白
¥2328
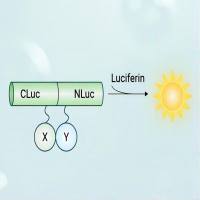
荧火素酶互补实验(Luciferase Complementation Assay, LCA)| 荧光素酶互补成像技术(Luciferase Complementation Imaging, LCI)
¥5999

