Cardiomyocytes From Human and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Zika virus (ZIKV) (strain Zika SPH2016) ZIKV-E (Stem/anchor domain of flavivirus envelope glycoprotein E) protein (Fc Tag)
¥4520
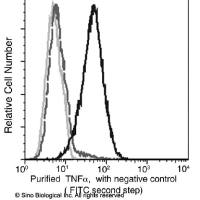
TNF-alpha / TNFA / TNFSF2 Antibody, Mouse MAb | TNF-alpha / TNFA / TNFSF2 鼠单抗
¥800

IL-2重组蛋白|Recombinant Human IL2 Protein
¥1080

MKN45人低分化胃癌细胞|MKN45细胞(Human Poorly Differentiated Gastric Cancer Cells)
¥1500

Recombinant-Human-Zinc-transporter-9SLC30A9Zinc transporter 9; ZnT-9 Alternative name(s): Human embryonic lung protein; HuEL Solute carrier family 30 member 9
¥13832
相关问答

