Human natural killer (NK) cells express an array of inhibitory and activating receptors some of which interact with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. Expression of these receptors varies at a clonal level generating subsets of NK cells with respect to their recep ...
It is now commonly accepted that natural killer (NK) cells are closely related to T cells. Some severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) patients have been described lacking T and NK cells, but having normal numbers of B and myeloid cells, suggesting a common origin of T and NK cells (1). Furthermore, T and ...
Individual natural killer cells express diverse combinations of cell surface receptors, including members of the killer cell immunoglobulin (Ig)-like receptor (KIR) family and of the CD94/NKG2 receptor type. Thus, it is often difficult to assign a precise ligand specificity to any giv ...
The exquisite specificity of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) has made them extremely versatile tools for scientific, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes. However, their production is time consuming and requires the immunization of animals and the subsequent use of rodent cells. Th ...
A limitation in the ability to analyze the function of the natural killer cell Ly49 and other receptors is the lack of antibodies to most of them. Even when monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have been generated, they do not always react with a given receptor from all strains of mice. For example, 5E6 binds to Ly49C ...
Upon proper stimulation (e.g., crosslinking FcγRIIIA , interaction with antibody -nonsensitized target cells, cytokines), mature natural killer (NK) cells produce and release cytokines involved in the modulation of immune responses (reviewed in refs. 1,2), including interfer ...
Natural killer (NK) cells constitute an important frontline defense against a range of viruses including herpes viruses, human immunodeficiency virus type 1, and hepatitis viruses (1). NK cell deficiencies can lead to serious, life-threatening virus infections, with herpesvirus ...
Natural killer (NK) cells mediate target cell lysis by two independent pathways, one involving exocytosis of preformed granules (which contain perforin and granzymes A and B), the other requiring ligation of CD95 on target cells with CD95 (APO-1/Fas) ligand on the effector cell (1–3). Both proc ...
Natural killer (NK) cells are able to identify and destroy target cells with absent or altered major histocomaptibility complex (MHC) class I, thereby mediating “natural cytotoxicity.” They also have the capacity to kill antibodycoated target cells by antibody-dependent cellular c ...
The ability to study the properties and functions of individual cells is a major goal of cell biologists. Nowhere is this more true than in studies of the immune system, in which the complexity is such that results obtained at the population level often obscure critical aspects of the function and dive ...
Natural killer (NK) cells kill their targets by inducing two distinct modes of cell death—apoptosis and necrosis (1–4). The end result in both cases is target cell lysis, broadly defined as a loss of membrane integrity and most usually assessed by either chromium release or uptake of certain nonvit ...
The natural killer (NK) cell has been shown to be important in mounting a host’s initial response to many types of invaders, such as certain types of viruses, bacteria, and protozoa, and to be involved in the control of neoplastic growth and in allograft rejection (1,2). However, before any leukocyte can p ...
Our understanding of the phenotypical and functional heterogeneity of human natural killer (NK) cells has greatly advanced over the past few years. This advancement has been greatly helped by the development of culture conditions for clonal proliferation of NK cells. Analysis of human NK ...
第一节 概念这里想明确两个概念,一个是Transwell,另一个是肿瘤细胞侵袭模型。1. Transwell关于Transwell这个词该如何解释,查了很多资料也未见准确的注解,我觉得可以这么理解吧,trans-这个词根有转移、转运、穿过等意思,well有小室的意思,可以从字面上理解,这是一类有通透性的杯状的装置,根据Corning公司的Transwell说明书中的介绍,可以认为这是一种膜滤器(Membrane filter ...
相关专题 生物帮之抗体制备 中国国民核生化灾害防护国家重点实验室防化研究院的研究人员利用elisa技术以剧毒生物毒素相思子毒素(Abrin)为检测对象,建立了一种高灵敏的电化学发光免疫检测方法。该论文已发表于近期的《分析化学》杂志上。 相思子毒素电化学发光检测原理:a. 多抗; b. 相思子毒素; c. 生物素化单抗; d. 三联吡啶钌; ...
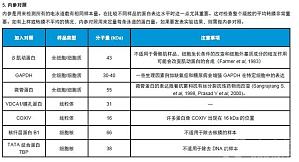
随着生命科学的发展,围绕蛋白进行的研究越来越多,抗体试剂在实验中的重要性越来越举足轻重。面临着纷呈复杂的抗体试剂市场,如何选择到适合自己实验的抗体就变得尤为重要。 一、关于特异性的选择 特异性的选择主要需要考虑四个方面:蛋白特异性、种属特异性、实验方法特异性、标记物的特异性。 1、蛋白特异性: 针对需要检测的蛋白查找抗体,几个细节要区分,重组表达的蛋白和内源性蛋白的检 ...
1. 为什么免疫后没有效价或免疫后效价低? 答:可以从这几个方面一一考虑: (1)设计的抗原与被免疫的动物内源蛋白有极高的同源性或者抗原是免疫原性极差的小分子物质。对于前一种情况应该重新设计抗原,设计抗原时尽量选取目标蛋白特异性的序列,可以设计为短肽然后再与载体蛋白偶联之后免疫;对于后一种情况,首先确认小分子物质是否已经正确地和载体蛋白偶联,如果偶联没有问题,可以更换其它的载体蛋 ...
一个脾脏中,能分泌抗体的细胞占的比例很少,90%以上的细胞是不能分泌抗体的。即使进行了人工免疫,能分泌出针对人工免疫的抗原的抗体的细胞占能分泌抗体的细胞的比例也是很低的。因此,尽管一个成功免疫的脾脏可达到2×108个细胞以上,但进行了细胞融合后能得到目标杂交瘤的数量也是很有限的,如何筛选出这些能分泌目的抗体的杂交瘤是一个非常关键的问题。 一般来说, 制备单抗的目的决定了 ...
关于动物免疫,在多抗制备一部分里已经作了一些讲解(点击这里查看),这里只简要讲述一下单抗制备中需要注意的几个问题。在概述部份已经讨论过,用来制备单抗的动物主要有小鼠、大鼠和兔,由于小鼠易饲养、小鼠单抗技术成熟、路线简单,因此是制备单抗使用的主流动物,这里主要以小鼠单抗制备展开讲述。 免疫途径和周期:单抗制备中,免疫动物的方式一般第一针采用皮下免疫,后面的加强免疫采用腹腔免疫、腘内免 ...
制备好抗原后,就要进行动物免疫了,免疫这一步除了动物自身的因素外,实验者也要有良好的计划才能得到更好的免疫效果。这里就几个常见的问题作一下简单的讨论。 动物的选择 常见的可以用来制备抗体的动物有:小鼠(Mouse)、大鼠(Rat)、豚鼠(Guinea pig)、仓鼠(Hamster)、兔(Rabbit)、绵羊(Sheep)、山羊(Goat)、马(Horse)、驴(Donkey)、奶 ...