在过去 30 年中,荧光染色体分析技术促进了人们对基因组构造的了解,并加深了对 DNA 的组织结构及染色体进化的认知。通过荧光染色,即便小型染色体也可以检出,并且可以获知其组分、形态结构及进行染色体计数,可以确认物种、选系和单株的染色体非整倍性及多倍性,包括杂交或组培及遗传转化导致的染色体变异。
在过去的 25 年里,转基因植株中外源基因插入模式和位点的研究,极大地有助于人们认识植物核基因组中外源基因的整合、表达和稳定遗传的机理。同时,分子鉴定对于转基因作物的安全评估也是一个必要的步骤。因此,本章主要介绍通过根癌农杆菌介导转化,或外源 DNA 直接转化方法所获得转基因禾谷类作物和牧草中,外源基因插入模式和位点数目的标准分析流程及鉴定方法。基因组中外源基因的数目和分布情况,主要通过遗传研究、PCR 和 Southern 分析相结合的方法进行鉴定。但是,仅仅依靠这些方法,并不足以完全掌握外源基因在植物中的分布情况,如要进行精确鉴定,还需借助其他试验方法的综合分析。本章并未对这些额外方法进行详细描述,仅提供相关书籍以供读者参阅。
通过转录后水平基因沉默(PTGS) 使内源基因下调表达是鉴定植物基因功能的一把钥匙。在植物、真菌和动物界不同的物种中已经发现许多基于 RNA 水平的沉默机制,如转录后水平基因沉默、共抑制、基因压制和 RNA 干扰(RNAi ) 。其中,RNAi是最令人感兴趣的发现之一。它是一种由双链 RNA ( dsRNA) 引发的、具有序列特异性的基因沉默机制,将与目的基因序列同源的双链 RNA 导入体内,可引起该基因编码的 mRNA 降解。用改造的病毒侵染植物也能诱导 RNA 沉默,称之为病毒诱导的基因沉默(VIGS) 。与插入突变相比,这些新兴的反向遗传学方法为在大麦和小麦等谷物物种中挖掘功能基因和操控基因的表达提供了更有力的实验工具。本章介绍如何在大麦和小麦中运用 RNAi 和 VIGS 技术研究基因的功能,包括该过程涉及的分子机制及常用的材料和方法,如载体、接种过程和沉默表型分析。
利用转基因手段为主的反向遗传学实验设计时,通常要求外源基因按照预先设定的模式进行表达,而有关特定启动子的基因表达谱信息则很有限。鉴于相同的启动子-转基因构建在不同的物种中可产生不同的表达模式,预先确定待转化外源基因的表达模式就显得尤为重要。本章就禾谷类作物已鉴定的组成型、特异型或诱导型启动子进行了比较。
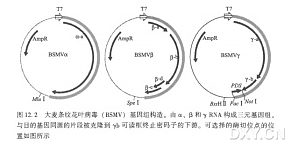
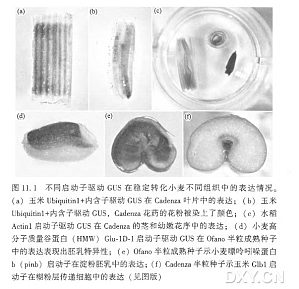
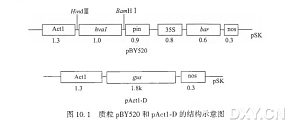
燕麦是一种在全球广泛种植的温带禾谷类作物,对干旱和/或高盐造成的渗透胁迫缺乏耐受能力。为了实现对现有商业化的燕麦栽培品种的遗传转化,我们建立了一套不受基因型影响的高效茎尖分生组织再生体系,4个燕麦品种 Prairie、Porter、Ogle和 Pacer 都能在体外高效地从茎尖分生组织分化出再生苗。应用这一再生体系,我们用基因枪对3个燕麦品种进行了质粒 pBY520 (带有 hva1 和 bar)和 pActl-D(带有gus)的共转化。用除草剂抗性和GUS作为标记,选择转基因阳性株系。用分子和生化的方法分析可能的转基因阳性株系,发现其中 100% 的植株带有 hva1和 bar基因,61.6%的植株同时带有三个基因(hva1、bar和进一步分析R0、R1、R2代转基因植株,显示三个基因都已稳定地整合到基因组中,其分离比符合孟德尔遗传。组织化学分析显示,在维管组织和成熟颖花的花粉粒中GUS表达水平较高。免疫化学分析显示hva1 在各个发育时期组成型表达,不过在苗早期表达水平较高。 我们分析了燕麦转基因后代 HVA1 的表达对其体内及体外渗透胁迫耐受性的影响。转基因燕麦对胁迫条件的耐受
高通量测序技术已广泛应用于植物研究中,但植物材料中较多的蛋白质、多糖以及酚、脂类等次生代谢物质,提取核酸的难度往往比动物或原核生物样本大,因此如何从植物样本中得到高质量的核酸进行后续的测序,成为在植物高通量测序应用中的首要因素。根据核酸类型,可有如下制备方法可参考:1. 植物基因组 DNA主要应用于植物的全基因组测序、重测序等。植物的全基因组测序要求基因组 DNA 量至少在 50~100 μg,可采用经典的 CTAB 抽提方法,配方和步骤如下: ...
荧光素酶自然界中的荧光素酶:是自然界中能够产生荧光的酶的系统,如发光真菌,发光海星,发光鱼,发光节虫,发光甲虫等。萤火虫荧光素酶:目前常用的萤火虫荧光素酶来源于北美萤火虫(Photinus pyralis),是一个61KDa的单体酶,无需表达后修饰,直接具有完全酶活性,反应需要底物荧光素以及ATP、氧气、镁离子等。海肾荧光素酶:来源于海肾(Renilla reniformis),是一个36KDa的单体酶,表达后无需修饰,即可具 ...
一、实验设计的意义实验设计是科学研究计划内关于研究方法与步骤的一项内容。在医学科研工作中,无论实验室研究、临床疗效观察或现场调查,在制订研究计划时,都应根据实验的目的和条例,结合统计学的要求,针对实验的全过程,认真考虑实验设计问题。一个周密而完善的实验设计,能合理地安排各种实验因素,严格地控制实验误差,从而用较少的人力、物力和时间,最大限度地获得丰富而可靠的资料。反之,如果实验设计存在着缺点,就可能造成不应有的浪费 ...
植物组织培养基包括多种成分:无机盐、维生素、氨基酸、生长调节剂、糖类、琼脂(或结冷胶)和水。所有这些成分在植物组织培养中至少有1种或多种作用。植物组织培养基中的矿质元素进入植物细胞后用于合成有机分子或作为酶反应中的催化剂。可溶性盐离子在植物电离分子运输中作为平衡离子,渗透压的调节以及维持植物体电化学势的平衡都起着重要的作用。氮、硫和磷是蛋白质和核酸的组成成分。镁离子和许多的微量元素是许多酶和细胞器的基本组成部分, ...
Fluorescent-based technologies offer opportunities for developing new assays for detection, quantification, and characterization of viral isolates. According to the intrinsic characteristics of fluorescent-based tools (high specificity, sensitivity, and relia ...
miRNAs have emerged as key regulators of gene expression in both plants and animals. These small (generally 21–22 nt) RNA molecules, originated from primary “hairpin” transcripts, can induce translational suppression or direct mRNA cleavage. Similar to regular mRNAs, the expression of ...
Non-invasive microelectrode ion flux measuring (the MIFE system) allows concurrent quantification of net fluxes of several ions with high spatial (several μm) and temporal (ca 5 s) resolution. Over the last 10 years, the MIFE system has been widely used to study various aspects of salt stress sig ...
Nearly all signal transduction pathways lead to regulation of gene expression by controlling specific transcription factors (TFs). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a powerful method for studying TF–DNA interactions in vivo. To identify all binding sites of a TF in the genome, t ...
Chimeric REpressor gene Silencing Technology (CRES-T) is a useful tool for functional analysis of plant transcription factors. In this system, a chimeric repressor that is produced by fusion of a transcription factor to the plant-specific EAR-motif repression domain (SRDX) suppres ...
Chloroplasts are metabolically important organelles that perform many essential functions within plant cells. The chloroplasts can be subdivided into six distinct sub-compartments to which a protein may be ultimately targeted. These sub-compartments are defined as the outer e ...
Soil salinity reduces the ability of plants to take up water, and this quickly causes reductions in the rate of cell expansion in growing tissues. The slower formation of photosynthetic leaf area in turn reduces the flow of assimilates to the meristematic and growing tissues of the plant. Later, salt ...
Genome-wide quantitative profiling of chromatin modifications is a critical experimental approach to study epigenetic and transcriptional control mechanisms. Since first being reported in 2007, chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequenci ...
Histone modifications play an essential role in chromatin-associated processes including gene regulation and epigenetic inheritance. It is therefore very important to quantitatively analyze histone modifications at both the single gene and whole genome level. Here, we descr ...
Methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism (MSAP) is a technique developed for assessing the extent and pattern of cytosine methylation and has been applied to genomes of several species (Arabidopsis, grape, maize, tomato, and pepper). The technique relies on the use of isoschizo ...
The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction is used to simultaneously amplify and quantify a targeted DNA molecule. It can be used to determine exact copy number of a molecule within a sample and/or to compare the quantity of a molecule between samples. When combined with reverse tran ...