相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 英文名:
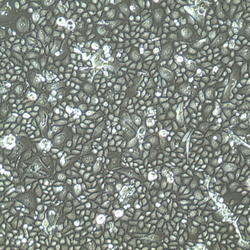
Endometrial (Uterine) Epithelial Cells
- 细胞类型:
人正常原代细胞
- 物种来源:
人源
- 器官来源:
人源
- 运输方式:
干冰或液氮
- 年限:
液氮储存10年以上
- 生长状态:
冻存
- 规格:
500,000 cells/vial
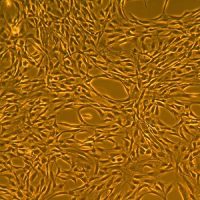
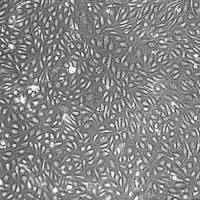
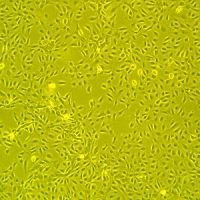
Lifeline® Normal Human Endometrial (Uterine) Epithelial Cells, when grown in Lifeline® ReproLife™ Medium, provide an ideal serum-free culture model for many areas of research. These cells may be used to study cellular physiology of the reproductive tract, the cellular response to infectious agents, and other areas of research.
Endometrial Epithelial Cells have been isolated, plated, and expanded in culture vessels three times before being harvested for cryopreservation to ensure the highest purity, viability and plating efficiency.
Lifeline® female reproductive epithelial cells are quality tested in ReproLife™ Medium to ensure optimal morphology and growth over a period of at least 5 population doublings.
Epithelial Cells are not exposed to antimicrobials or phenol red when cultured in ReproLife™ medium. Although Lifeline® offers antimicrobials and phenol red, they are not required for eukaryotic cell proliferation.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验Analysis of Uterine Natural Killer Cells in Mice
regarding this cell lineage. These approaches identified the special angiogenic properties of uNK cells and their regulatory relationships with normal physiological changes to the uterine (endometrial) arterial tree that accompany successful pregnancy. This chapter
It is likely that adult epithelial stem cells will be useful in the treatment of diseases, such as ectodermal dysplasias, monilethrix, Netherton syndrome, Menkes disease, hereditary epidermolysis bullosa, and alopecias. Additionally
Viral Transformation of Epithelial Cells
Approximately 18% of human cancers have a viral etiology and the majority of these involve transformation of epithelial cells. Viral proteins transform epithelia by inducing alterations in the normal cell growth and differentiation pathways