相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 运输方式:
冻存运输
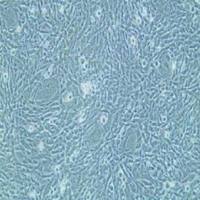
- 细胞形态:
球形
- 库存:
大量
- 年限:
3.5 days embryo, blastocyst
- 器官来源:
胚胎
- 生长状态:
贴壁生长
- 组织来源:
inner cell mass
- 品系:
129X1 x 129S1
- ATCC Number:
SCRC-1011™
- 物种来源:
小鼠
- 是否是肿瘤细胞:
0
- 细胞类型:
胚胎干细胞
| Designations: | R1 | ||
| Depositors: | A Nagy | ||
| Biosafety Level: | 1 | ||
| Shipped: | frozen | ||
| Medium & Serum: | See Propagation | ||
| Growth Properties: | adherent | ||
| Organism: | Mus musculus | ||
| Morphology: | spherical colony |
||
| Source: | Organ: embryo Strain: 129X1 x 129S1 Tissue: inner cell mass Cell Type: embryonic stem cell; |
||
| Permits/Forms: | In addition to the MTA mentioned above, other ATCC and/or regulatory permits may be required for the transfer of this ATCC material. Anyone purchasing ATCC material is ultimately responsible for obtaining the permits. Please click here for information regarding the specific requirements for shipment to your location. | ||
| Restrictions: | Prior to purchase, for-profit commercial institutions must obtain a license agreement. For instructions on how to proceed, please contact ATCC 's Office of Licensing and Business Development at licensing@ATCC .org or 703 365 2773. | ||
| Isolation: | Isolation date: August, 1991 | ||
| Applications: | However, about 20% of subclones derived from passage #14 had the original developmental potential of R1 when tested by tetraploid aggregates [PubMed: 8378314]]. No live offspring were produced from cells older than passage #14.* . Pluripotency of R1 was initially tested by tetraploid embryo <-> ES aggregates for completely ES derived development [PubMed: 8378314]. The R1 cell line was established in August 1991, from a 3.5 day blastocyst produced by crossing two 129 substrains (129S1/SvImJ and 129X1/SvJ). The segregation could result in several coat types, from albino, through light brown, to black, depending on the genetic background of the partner of the germline chimaera. |
||
| Age: | 3.5 days embryo, blastocyst | ||
| Gender: | male | ||
| Comments: | The R1 cell line was established in August 1991, from a 3.5 day blastocyst produced by crossing two 129 substrains (129S1/SvImJ and 129X1/SvJ). The cells are heterozygous for the c locus (+/c (ch)) and for the pink eye locus (+/p). In the F1 generation the coat color is uniform agouti, while in the F2 these two coat color genes segregate. The segregation could result in several coat types, from albino, through light brown, to black, depending on the genetic background of the partner of the germline chimaera. Pluripotency of R1 was initially tested by tetraploid embryo <-> ES aggregates for completely ES derived development [PubMed: 8378314]. They were also tested by diploid embryo <-> ES aggregates and blastocyst injection for germline transmission in chimeras [PubMed: 8361547]. At early passages (up to passage #14), one third of the completely R1-derived newborns generated by tetraploid embryo <-> R1 aggregates survived. No live offspring were produced from cells older than passage #14.* . However, about 20% of subclones derived from passage #14 had the original developmental potential of R1 when tested by tetraploid aggregates [PubMed: 8378314]]. R1-derived animals reached adulthood and were fertile. The genetically altered lines derived from R1 gave high efficiency of germline transmission either by injecting them into C57 blastocyst or aggregating them with CD-1 or ICR outbred 8-cell stage embryos. More than 90% of the individual K.O. clones went to germline (n>60) by aggregation chimeras. *Current ATCC stocks of R1 cells are beyond passage 14. Current stocks of alternative subclone of R1 cells, designated R1/E (ATCC SCRC-1036 ), are below passage 14 and have been shown to be germline competent. |
||
| Propagation: | ATCC complete growth medium: Mouse ES Cell Basal Medium Atmosphere: air, 95%; carbon dioxide (CO2), 5% Temperature: 37.0°C |
||
| Subculturing: | Protocol: Establishing and maintaining your culture: To insure the highest level of viability, be sure to warm media to 37�C before using it on the cells.
Interval: Every one to two days Subcultivation Ratio: A subcultivation ratio of 1:4 to 1:7 is recommended Medium Renewal: Every day |
||
| Preservation: | Freeze medium: Complete growth medium supplemented with an additional 10% FBS and 10% DMSO. Storage temperature: liquid nitrogen vapor phase |
||
| Related Products: | Derivative: ATCC SCRC-1036 | ||
| References: | 57459: Matise M, et alProduction of targeted embryonic stem cell clonesIn: Matise M, et alGene Targeting: A Practical ApproachOxfordOxford University Press101-132, 1999 71506: Nagy A, et al. Derivation of completely cell culture-derived mice from early-passage embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA : 8424-8428, 1993. PubMed: 8378314 71870: Wood SA, et al. Non-injection methods for the production of embryonic stem cell-embryo chimaeras. Nature 365: 87-89, 1993. PubMed: 8361547 71871: Nagy A, Rossant JProduction and analysis of ES-cell aggregation chimerasIn: Nagy A, Rossant JGene Targeting: A Practical ApproachOxfordOxford University Press177-206, 1999 |
||
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验相关专题 以下是根据NIH老年病研究所 提供的英文的R1胚胎干细胞培养protocol整理而成。根据经验作部分修改。 1、一般培养:保持胚胎干细胞 处于未分化状态 培养基细胞复苏冻存细胞明胶包被细胞传代 2 、体外分化 培养基包被有多聚鸟氨酸/纤维结合蛋白的培养板(使用或不使用盖玻片) 体外分化方法 注:以下培养针对于小鼠的R1胚胎干细胞系,其它胚胎
在生化室日常工作中,大家会发现:在双试剂测试项目中,总是R2用完了,而R1尚余很多,随着检验次数的累积, 这种效应越加明显,留下来的R1留之无用, 弃之可惜。 生化试剂R1、R2消耗量不对等的原因: 如果查阅仪器说明书,可以发现生化试剂在使用过程中是有损耗的,这种效应是由于仪器本身设计有试剂 ”取样/ 富余量“所致,多数仪器都存在这种问题。 仪器在试剂瓶转移到反应杯的过程中,会多吸入大概5ul的量
人可溶性肿瘤坏死因子受体-1(sTNF-R1)ELISA试剂盒 说明书
上海西唐生物科技有限公司 021-55229872, 65333639 www.westang.com 人可溶性肿瘤坏死因子受体-1 (sTNF-R1)ELISA 试剂盒 ( 用于血清、血浆、细胞培养上清液和其它生物体液内 ) 原理 本实验采用双抗体夹心 ABC-ELISA 法。用抗人 sTNF-R1 单抗包被于酶标板上,标准品和样品中的 sTNF-R1与单抗结合
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料