万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 服务名称:
人源细胞株鉴定
- 提供商:
苏州鉴达生物科技
- 规格:
1200元/株
近年来,大量研究表明STR基因分型方法是进行细胞交叉污染和性质鉴定的最有效和准确的方法之一,STR基因分型应用于细胞鉴定已被ATCC等机构强烈推荐。
我公司推出了细胞STR鉴定服务并与多家研究机构、细胞中心、生产厂商等建立长期合作关系。现行技术科同时分析多个STR基因座,可以准确的判断交叉污染和细胞类型。微量样本即可满足检测需求,并且可以检测到早期污染。
1、细胞送样要求:
特别提醒:目前只针对人源细胞进行STR鉴定,非人源细胞暂不受理。
拟进行的细胞鉴定的客户首先应在ATCC等官方网站查询需要鉴定的细胞有没有被ATCC等数据库收录,不详之处可咨询公司在线客服。同时请将以下信息发给我公司在线客服:单位名称(发票抬头)、课题负责人(老板)姓名、电话及电子邮箱。公司将拟好的委托合同发送至客户,负责人在合同上签字后和细胞悬液一起快递至公司。
2、送检细胞:
将1×10的五次方以上细胞悬液置于1.5毫升EP管,用封口膜密封,管壁标记清楚细胞的名称(如HepG2),数量较多时可用编号,并附送检清单。随委托合同一起快递至我公司即可(细胞状态与STR检测无关,请放心邮寄)。
3、细胞株鉴定收费标准:
高等院校及科研机构1200元/株,其他机构或个人:1440元/株。细胞株数量大于50的机构另行议价。
4、检测时限:
正常情况下,收到样本后一个工作日完成检测,并出具正式检测报告。
5、报告形式:
针对细胞株鉴定,本公司将出具英文版报告,可直接用于外文杂志投稿。可联系公司在线客服索取报告模板及样式。
6、标注优惠政策:
如客户在发表的高水平SCI论文(IF>8)中标注细胞株鉴定由我公司完成,我们承诺为客户免费检测两株细胞株。标注格式如下:The cell lines were characterized by Genetic Testing Biotechnology Corporation (Suzhou, China) using short tandem repeat (STR) markers.
7、利用苏州鉴达生物科技细胞株鉴定服务发表的部分高水平(IF>5)论文(截止2023-12-18)
[1]. Ren A et al., Int J Cancer. 2019 Jul 1;145(1):154-163. PMID: 30561001
[2]. Shen Y et al., Int J Cancer. 2019 Feb 1;144(3):651-664. PMID: 30289981
[3]. Xu H et al., Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 4. pii: clincanres.2363.2018. PMID: 30610101
[4]. Li B et al., Stem Cells. 2018 Oct 23. PMID: 30353595
[5]. Shi J et al., Mol Pharm. 2018 Sep 4;15(9):4139-4147. PMID: 30048594
[6]. Li B et al., Oncogene. 2018 Oct;37(41):5508-5519. PMID: 29895968
[7]. Yuan Y et al., Int J Cancer. 2018 Jul 10. PMID: 29987896
[8]. Yu J et al., J Hepatol. 2018 Jun;68(6):1214-1227. PMID: 29378234
[9]. Zhang N et al., Cell Death Differ. 2018 Jul 9. PMID: 29988076
[10]. Du L et al., Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jun 18;9(7):714. PMID: 29915309
[11]. Zhou P et al., J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 2;36(1):115. PMID:28865485
[12]. Wang X et al., Int J Cancer. 2017 Jun 28. PMID: 28656647
[13]. Li Y et al., Nat Commun. 2017 Aug 24;8(1):347. PMID: 28839186
[14]. Wang C et al., Carcinogenesis. 2017;38:168-76. PMID:28034876
[15]. Wang X et al., Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(12):e2517. PMID:27929537
[16]. Li P et al., Oncogenesis. 2017 Apr 24;6(4):e322. PMID:28436991
[17]. Du J et al., Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Feb;17(2):419-431. PMID: 28864683
[18]. Chen L et al.,Nat Commun. 2017 Jul 17;8:16066. PMID:28714476
[19]. Li H et al., Cancer Lett. 2018 Sep 28;432:121-131. PMID: 29890207
[20]. Lu-Hua Zhang et al., Neuro Oncol. 2020 Jun 3;noaa138. PMID: 32492707
[21]. Ke Nie et al., Oncogenesis. 2020 May 15;9(5):51. PMID: 32415061
[22]. Si-Jing Li et al., Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(12):3864. PMID: 33371368
[23]. Xiaolong Zhang et al., Cancer Sci. 2020;111(10):3802-3812. PMID: 32691974
[24]. Xiaoying Hou et al., 2018;9:21. PMID: 29472856
[25]. Biao Geng et al., J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):208. PMID: 30165890
[26]. Tao Gui et al., Cell Death Differ. 2021 Jun 26. PMID: 34175897
[27]. Jie Xiong et al., EBioMedicine. 2021 Oct 7;72:103614. PMID: 34628354
[28]. Haitao Zhang et al., Elife. 2021 May 14;10:e64943. PMID: 33988507
[29]. Shourong Wu et al., Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 15;78(16):4549-4562. PMID: 29921695
[30]. Huiying Han et al., Blood. 2021 Mar 25;137(12):1603-1614. PMID: 32967010
[31]. Sha Song et al.,Oncogene. 2021 Sep;40(35):5393-5402. PMID: 34274946
[32]. Xin Chen et al., Mol Cancer Ther. 2022 Jan;21(1):149-158. PMID: 34725191
[33]. Sichong Han et al., Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jun;188:114539. PMID: 33819468
[34]. Huai Wang et al., Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021 Sep;1868(10):119084. PMID: 34166715
[35]. Ke Gong et al., Cancer Lett. 2022 Jan 28;531:27-38. PMID: 35093426
[36]. Li-Juan Deng et al., J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113443. PMID: 33022344
[37]. Herong Cui et al., Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105242. PMID: 33075491
[38]. Xingwen Wang et al., Mol Ther. 2022 Jan 8;S1525-0016(22)00014-4. PMID: 35017116
[39]. Yiran Liang et al., Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids. Vol. 23 December 2021
[40]. Xiwang Yang et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Feb 1;119(5):e2110428119. PMID: 35091468
[41]. Xingzhou Wang et al., Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 21;8:592919. PMID: 33553141
[42]. Caiqiong Liu et al., Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 16;12:658236. PMID: 33935780
[43]. Sichong Han et al., Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 23;22(1):60. PMID: 33374641
[44]. Renjian Xie et al., Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 12;23(2):794. PMID: 35054979
[45]. Fuwei Cheng et al., J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jan 24. PMID: 35075768
[46]. Yong Yi et al., Liver Int. 2021 Jun;41(6):1409-1420. PMID: 33506565
[47]. Qiang Hou et al., Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Feb 18;14:1131-1145. PMID: 33633453
[48]. Li Liang et al., Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 25;21(1):135. PMID: 33632198
[49]. Bing Yao et al., Genome Med. 2021 Apr 14;13(1):58. PMID: 33853662
[50]. Dong Zhao et al., Oncogene. 2022 Feb 15. PMID: 35169254
[51]. Xuan Deng et al., Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 13;12(5):485. PMID: 33986248
[52]. Wenjie Ge et al., Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jul 26;7(1):195. PMID: 34312379
[53]. Huijing Yin et al., Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 9;12(1):4230. PMID: 34244494
[54]. Hai-Yan Peng et al., Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, Vol. 18
[55]. Xiaoqing Zhang et al., Oncogene. 2021 Sep;40(35):5427-5440. PMID: 34282273
[56]. Qiongya Zhao et al., Diabetes. 2022 Feb 1;71(2):233-248. PMID: 34810178
[57]. Shun Li et al., Biofabrication. 2021 Aug 31;13(4). PMID: 34407511
[58]. Xiaomin Yin et al., Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 25. PMID: 35879403
[59]. Shuaifeng Li et al., Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 17;13(1):3486. PMID: 35710796
[60]. Qi Zhou et al., Mol Cell. 2022 Nov 8;S1097-2765(22)01058-9.PMID: 36384136
[61]. Sha Song et al., Br J Cancer. 2023 Apr;128(6):1086-1094.PMID: 36593359
[62]. Xiaojun Ren et al., Cell Discov. 2023 Jul 25;9(1):76.PMID: 37488138
[63]. Kaiyuan Wang et al., Nat Commun. 2023 May 23;14(1):2950. PMID: 37221157
[64]. Xiaoling Hong et al., Cell Death Dis. 2023 Feb 10;14(2):100. PMID: 36765041
[65]. Wanzhou Wu et al., Cell Death Dis. 2023 Mar 6;14(3):183. PMID: 36878949
[66]. Xiangwei Zeng et al., NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023 Mar 15;7(1):28. PMID: 36922568
[67]. Xue Ding et al., Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 30;14(8):575. PMID: 37648688
[68]. Weimin Zhang et al., Apoptosis. 2023 Nov 24. PMID: 38001343
[69]. Wei-Feng Hong et al., Cancer Lett. 2023 Dec 1:578:216460. PMID: 37863352
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验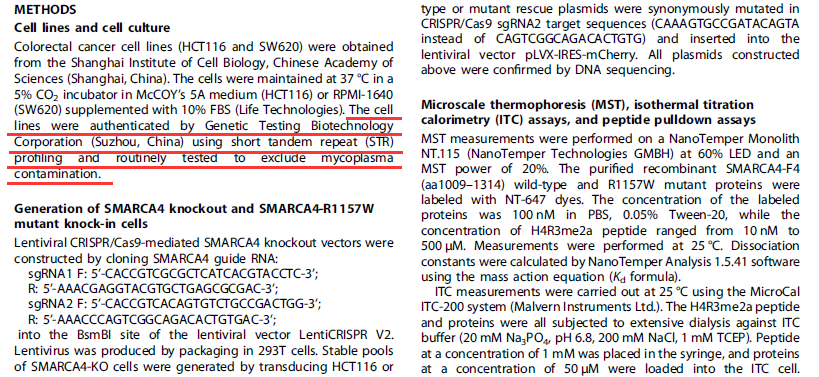
2. Xue Ding et al., NPM promotes hepatotoxin-induced fibrosis by inhibiting ROS-induced apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells and upregulating lncMIAT-induced TGF-β2. Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 30;14(8):575.

3. Wanzhou Wu et al., The TRPM7 channel reprograms cellular glycolysis to drive tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2023 Mar 6;14(3):183.

4. Xiaoling Hong et al., UBE2E2 enhances Snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant activity in ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis . 2023 Feb 10;14(2):100.
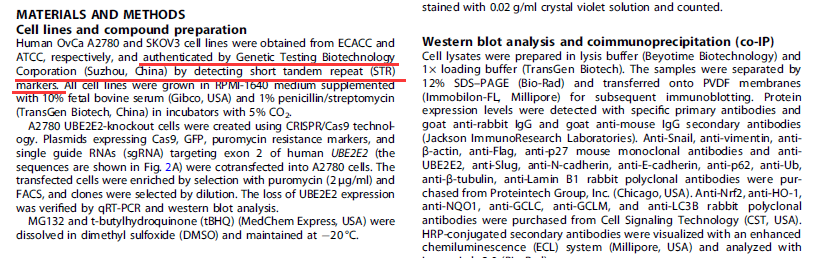
5. Weimin Zhang et al., Multiple myeloma with high expression of SLC7A11 is sensitive to erastin-induced ferroptosis. Apoptosis. 2023 Nov 24.

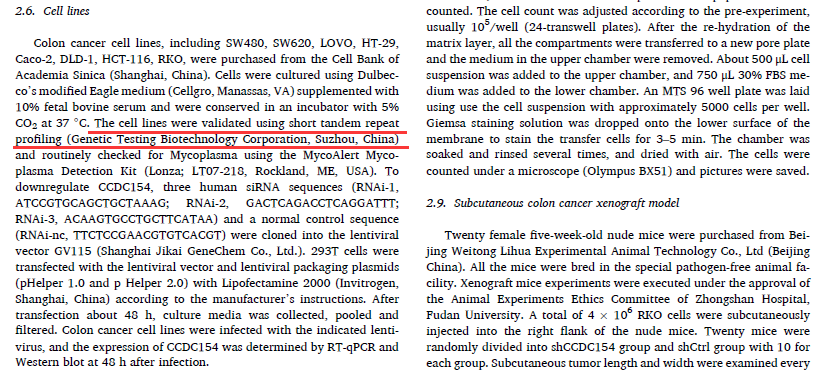
6. Wei-Feng Hong et al., Coiled-coil domain-containing 154 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis via interacting with minichromosome maintenance complex component 2. Cancer Lett. 2023 Dec 1:578:216460.
Authentication Techniques Whatever the scope of work to be carried out it is important to know that the work is being conducted using the correct reagents. This is no less important for cell cultures, since if cell cultures
Authentication of Cancer Cell Lines by DNA Fingerprinting
The requirement for authentication of cell lines has a history almost as long as cell culturing itself, presumably beginning when more then one cell line could be cultured continuously. The application of specific species markers, including
Authentication Techniques Whatever the scope of work to be carried out it is important to know that the work is being conducted using the correct reagents. This is no less important for cell cultures, since if cell cultures
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料










