Protocol for Analyzing Human Leukocyte Antigen Variants and Sexually Transmitted Infections: From Genotyping to Immunoassays
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐
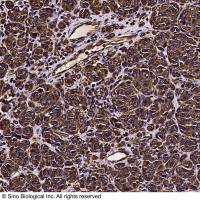
Vimentin Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified | Vimentin 兔多抗 (抗原亲和纯化)
¥1699

Recombinant-Bovine-E-selectinSELEE-selectin Alternative name(s): CD62 antigen-like family member E Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1; ELAM-1 Leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion molecule 2; LECAM2 CD_antigen= CD62E
¥12894

IL-2重组蛋白|Recombinant Human IL2 Protein
¥1080

免疫沉淀protocol
¥600

Spike S1 Neutralizing Antibody (B.1.617.2, B.1.617.2.1, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, B.1.429, and P.1 Variants) (Clone C-A11) (SARS-CoV-2)
询价
相关问答

