Sequencing of RAPD Fragments Using 3-Extended Oligonucleotide Primers
互联网
468
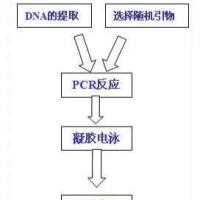
Both directed and nondirected techniques are used in population biology for the identification of the genetic source of variation and the genetic locus of disease or quality traits (1 ,2 ). The “nondirected” approaches use random genome scanning methods initially to generate polymorphic map markers, which then can be linked to traits of interest. One nondirected approach is random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers (2 -2 ), in which polymorphic polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products are amplified from genomic templates using monomer oligonucleotide primers, typically of 10 nt. Because RAPDs may be applied without prior sequence information, the technique is often used both for genome fingerprinting (2 -4 ) and for detailed genetic mapping (4 ,5 ) in organisms for which other genetic markers have not been developed. The conversion of mapped random markers into sequence characterized loci (STS) necessitates the isolation of the marker DNA fragment and the determination of its DNA sequence.