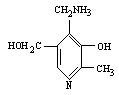
Pyridoxine Deficiency: Animal Model for CNS Serutonin and GABA Depletion
互联网
711
The term pyridoxine is generally used to refer to the group of naturally occurring pyridine derivatives represented by pyridoxine (pyridoxol), pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine, with similar physiological actions. They are referred to as vitamin B6 vitamers. Pyridoxine is used synonymously with vitamin B6 . Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is the major coenzymatic form of pyridoxine. There are over 100 known pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent reactions, most of which are involved in the metabolism of various amino acids. Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in the functioning of the nervous system. The putative neurotransmitters dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and taurine, as well as the sphingolipids and polyamines, are synthesized by PLP-dependent enzymes. There is considerable variation in the affinities of various apoenzymes for PLP. In view of this, during progressive pyridoxine deficiency, the PLP-dependent enzymes are decreased to various extents, from no decrease to almost a complete depletion. The decreases in the activities of glutamic acid and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylases during pyridoxine deficiency result in the reduction of the concentrations of the neurotransmitters GABA and 5HT.