Concurrent Assessment of Calpain and Caspase-3 Activity by Means of Western Blots of Protease-Specific Spectrin Breakdown Products
互联网
472
The calpains are found ubiquitously in mammalian cells and are activated following various central nervous system (CNS) insults,
including ischemia (1
), spinal cord injury (2
) and traumatic brain injury (TBI) (3
–5
). Nonerythroid α-spectrin is a submembrane cytoskeletal protein and preferred calpain substrate (6
). Calpain overactivation following TBI leads to rapid spectrin proteolysis that precedes and is thought to contribute to
cellular dysfunction and cell death (3
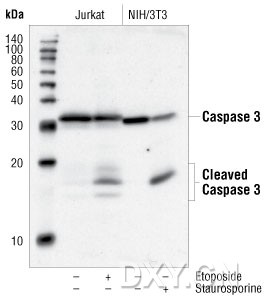
). In addition to cleavage by calpain, α-spectrin is also cleaved by caspase-3, a cysteine protease believed to be a key executioner
in apoptosis (7
). While both the calpains and caspase-3 produce an initial fragment of nearly identical size (150 kDa), these proteases also
produce distinct α-spectrin breakdown products; a 145-kDa fragment generated by calpain and a 120-kDa fragment generated by
caspase-3 (7
).