Quantitation of mRNA Levels by RT-PCR in Cells Purified by FACS: Application to Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Leukocyte Subsets
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Retinoic Acid and Retinoid X Receptors Antibody Sampler Kit
¥500
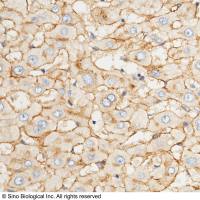
ACE2 兔多抗 | ACE2 Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified
¥800

PCNA细胞增殖检测试剂盒(ICF/FACS法);R41175-20T
¥1610

Recombinant-Chicken-Leukocyte-cell-derived-chemotaxin-1LECT1Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 1 Cleaved into the following 2 chains: 1. Chondrosurfactant protein; 2. CH-SP 3. Chondromodulin-1 Alternative name(s): Chondromodulin-I; ChM-I
¥9968

eGFP mRNA,1mg/ml,阿拉丁
¥6179.90
相关问答

