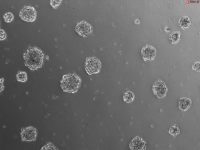
The disability and pain that result from damage to articular cartilage within the knee joint has stimulated the development of several approaches to facilitate the restoration of joint function (1 –9 ). Recently, cultured autologous chondrocytes, isolated from an individual’s own cartilage, have been expanded in vitro, and then implanted into the damaged site for repair of damaged knee cartilage (10 ). This remarkable process has been characterized by the modulation of gene expression during proliferation expansion and subsequent redifferentiation of cultured chondrocytes in vitro (11 ) and in vivo (12 ). Since the unique biomechanical properties of hyaline articular cartilage have been shown to be intimately linked with the biochemistry of the tissue (see Buckwalter and Mow ref. 13 for review), we have developed an in vitro system to verify that proliferatively expanded chondrocytes retain their ability to redifferentiate, or re-express their hyaline articular cartilage phenotype. Although the methods described herein were developed for specific application to chondrocytes, the principles for evaluation of biochemical and molecular biological properties of tissue-engineered materials, in vitro, may be applied to the development of any functional, high quality, tissue engineered implant.