Dye-Ligand Affinity Chromatography for Protein Separation and Purification
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Coronavirus Nucleocapsid重组蛋白|Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid-AVI&His recombinant Protein,Biotinylated
¥4520

Recombinant-Saccharomyces-cerevisiae-V-type-proton-ATPase-subunit-eVMA9V-type proton ATPase subunit e; V-ATPase subunit e Alternative name(s): Low dye-binding protein 10 Vacuolar proton pump subunit e
¥9436

SCF重组蛋白|Recombinant Human SCF / C-kit ligand Protein (aa 1-189, His Tag)
¥580
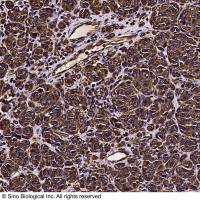
Vimentin Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified | Vimentin 兔多抗 (抗原亲和纯化)
¥1699

IL-2重组蛋白|Recombinant Human IL2 Protein
¥1080
相关问答

