Validating Pharmacological Disruption of ProteinProtein Interactions by Acceptor Photobleaching FRET Imaging
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Recombinant-Rat-Prenylated-Rab-acceptor-protein-1Rabac1Prenylated Rab acceptor protein 1 Alternative name(s): PRA1 family protein 1
¥10430

Cathepsin D and E FRET Substrate acetate,839730-93-7,≥98%,阿拉丁
¥1149.90
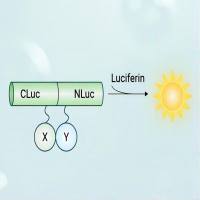
荧火素酶互补实验(Luciferase Complementation Assay, LCA)| 荧光素酶互补成像技术(Luciferase Complementation Imaging, LCI)
¥5999

Recombinant-Human-Prenylated-Rab-acceptor-protein-1RABAC1Prenylated Rab acceptor protein 1 Alternative name(s): PRA1 family protein 1
¥10430

Recombinant-Dog-Prenylated-Rab-acceptor-protein-1RABAC1Prenylated Rab acceptor protein 1 Alternative name(s): PRA1 family protein 1
¥10430

