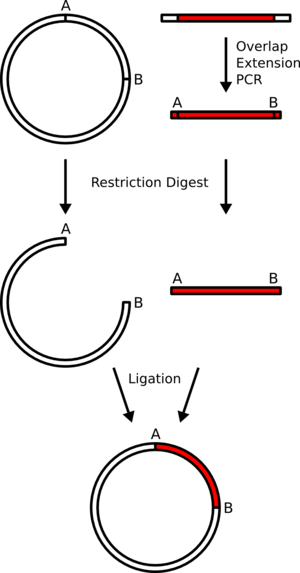
Subcloning for DNA Sequencing
互联网
548
Chemical (1 ) and enzymatic (2 ) methods for determining DNA sequences have revolutionized the techniques of molecular genetics and subsequently our understanding of the gene. The use of singlestranded Ml3 bacteriophage (3–5), in conjunction with Sanger’s dideoxy chain-termination sequencing procedure (2 ), has greatly increased the rate at which genes can be analyzed. One prerequisite for an efficient sequencing strategy is a set of subclones whose endpoints are evenly distributed along the entire sequence. Shotgun subcloning methods ((6 ),(7 )) require rigorous fractionation of the DNA fragments before cloning, to insure appropriately sized subclones in the final library. Since clones are then chosen at random from the library, shotgun methods are very inefficient at completing the last few small sequence gaps that remain near the end of the project. Various nonrandom subcloning methods have also been developed, utilizing partial restriction digests (8 ), BAL-3 1 digestion (9 ), exonuclease III digestion (l0–13), and DNase I (14 ).