Integron Analysis and Genetic Mapping of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Recombinant-Xenopus-tropicalis-Transmembrane-protein-173tmem173Transmembrane protein 173 Alternative name(s): Stimulator of interferon genes protein; STING
¥11704

A673_03341/A673_03341蛋白//蛋白/Recombinant Salmonella enterica OmpA family protein (A673_03341), partial重组蛋白
¥69
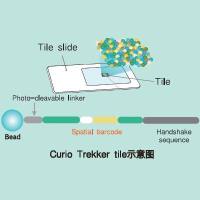
Trekker Single-Cell Spatial Mapping Kit 单细胞空间转录组分析试剂盒
询价

Recombinant-Saccharomyces-cerevisiae-Altered-inheritance-of-mitochondria-protein-11AIM11Altered inheritance of mitochondria protein 11 Alternative name(s): Genetic interactor of prohibitins 8
¥9996

Cell Cycle Analysis Kit (with RNase)(BA00205)-50T/100T
¥300
相关问答

