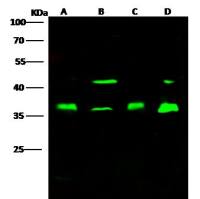
Analysis of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) Associated With DNA Excision Repair Sites in Mammalian Cells
互联网
579
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a homotrimeric protein adopting a ring structure that may encircle DNA. In this form, PCNA functions as a sliding platform to which different types of catalytic and regulatory proteins are tethered to perform DNA transactions such as replication and repair synthesis, methylation, chromatin assembly and remodeling, as well as sister chromatid cohesion. In addition, PCNA coordinates DNA metabolism with cell cycle progression by interacting with cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK), and CDK inhibitors. PCNA participates in different pathways of DNA repair, including nucleotide and base excision repair, as well as mismatch repair, by interacting with proteins involved in these processes. A fundamental step in DNA repair involves the transition of PCNA from a freely soluble nucleoplasmic form, to a chromatin-bound form associated with repair sites. This chapter describes biochemical and immunofluorescence methods for detection of the chromatin-bound form of PCNA involved in DNA repair. Cellular fractionation and nuclear extraction procedures are provided for Western blot analysis, as well as for protein-protein interaction studies. An in situ extraction protocol is described for immunostaining, fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometric analyses of nuclear localization, and cell cycle distribution of PCNA associated with DNA repair sites.