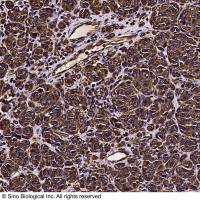
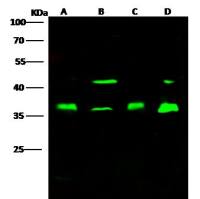
Immunohistochemical Detection of Cells in the Division Cycle Using Antibodies to Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA)
互联网
569
The detection and quantification of cells undergoing proliferation have centered on methods that identify specific stages of the cell cycle. Thus, the replication of DNA or S-phase (the labeling index) is detected by the use of [3 H]-thymidine and autoradiography, or by bromodeoxyuridine and immunohistochemical labeling. The other stage of the cell cycle that is frequently examined is mitosis, or M-phase (the mitotic index), via the use of spindle inhibitors, such as colchicine. These techniques detect only phases of the cell cycle and require that the animal or cell culture be dosed with [3 H]-thymidine or bromodeoxyuridine, or with colchicine. These parts of the cell cycle are of differing durations and do not give a direct measure of the growth fraction. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is an endogenous nuclear protein that functions as an accessory protein to DNA polymerase (pol) δ (1 ). Since PCNA is present in all cycling cells, the entire proportion of dividing cells present at any instant in a population can be detected (2 ,3 ).