Assessment of Cerebral Vascular Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐
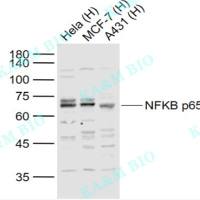
Traumatic Brain Injury Biomarker Antibody Sampler Kit
询价

Recombinant-Rat-Ninjurin-1Ninj1Ninjurin-1 Alternative name(s): Nerve injury-induced protein 1
¥10136

Recombinant-Mouse-Membrane-primary-amine-oxidaseAoc3Membrane primary amine oxidase EC= 1.4.3.21 Alternative name(s): Copper amine oxidase Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase; SSAO Vascular adhesion protein 1; VAP-1
¥15568

Recombinant-Human-Integral-membrane-protein-2CITM2CIntegral membrane protein 2C Alternative name(s): Cerebral protein 14 Transmembrane protein BRI3 Cleaved into the following chain: 1. CT-BRI3
¥11158
Traumatic Acid
¥807

