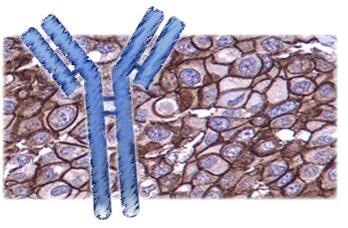
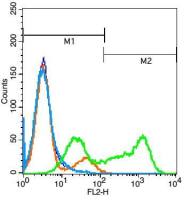
相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
上海联迈生物工程有限公司
- 库存:
大量
- 靶点:
详见说明书
- 级别:
1
- 目录编号:
LM-1040R-FITC
- 克隆性:
多克隆
- 抗原来源:
Rabbit
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
Anti-factor V/FITC
- 抗体名:
Anti-factor V/FITC
- 标记物:
FITC标记
- 宿主:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Pig,
- 适应物种:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Pig,
- 免疫原:
详见说明书
- 亚型:
IGg
- 形态:
粉末、液体、冻干粉
- 应用范围:
IF=1:50-200
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
-20 °C
- 规格:
100ul
| 英文名称 | Anti-factor V/FITC |
| 中文名称 | FITC标记的凝血因子5抗体 |
| 别 名 | Coagulation factor V heavy chain; activated protein C cofactor; coagulation factor V; F5; Factor V Leiden; FactorV; FVL; labile factor; proaccelerin; FA5_HUMAN; Proaccelerin, labile factor; Activated protein c cofactor; Coagulation factor V (proaccelerin, labile factor); Coagulation factor V; Factor V Leiden; PCCF. |
| 规格价格 | 100ul/2980元 购买 大包装/询价 |
| 说 明 书 | 100ul |
| 研究领域 | 心血管 细胞生物 免疫学 |
| 抗体来源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆类型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反应 | Human, Mouse, Rat, Pig, |
| 产品应用 | IF=1:50-200 not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 78kDa |
| 性 状 | Lyophilized or Liquid |
| 浓 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Coagulation factor V heavy chain |
| 亚 型 | IgG |
| 纯化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 储 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存条件 | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| 产品介绍 | background: This gene encodes coagulation factor V which is an essential factor of the blood coagulation cascade. This factor circulates in plasma, and is converted to the active form by the release of the activation peptide by thrombin during coagulation. This generates a heavy chain and a light chain which are held together by calcium ions. The active factor V is a cofactor that participates with activated coagulation factor X to activate prothrombin to thrombin. Defects in this gene result in either an autosomal recessive hemorrhagic diathesis or an autosomal dominant form of thrombophilia, which is known as activated protein C resistance. Function: Central regulator of hemostasis. It serves as a critical cofactor for the prothrombinase activity of factor Xa that results in the activation of prothrombin to thrombin. Subunit: Factor Va, the activated form of factor V, is composed of a heavy chain and a light chain, non-covalently bound. The interaction between the two chains is calcium-dependent. Forms heterodimer with SERPINA5. Subcellular Location: Secreted. Tissue Specificity: Plasma. Post-translational modifications: Thrombin activates factor V proteolytically to the active cofactor, factor Va (formation of a heavy chain at the N-terminus and a light chain at the C-terminus). Sulfation is required for efficient thrombin cleavage and activation and for full procoagulant activity. Activated protein C inactivates factor V and factor Va by proteolytic degradation. Phosphorylation sites are present in the extracellular medium. DISEASE: Factor V deficiency (FA5D) [MIM:227400]: A blood coagulation disorder leading to an hemorrhagic diathesis known as parahemophilia. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance (THPH2) [MIM:188055]: A hemostatic disorder due to defective degradation of factor V by activated protein C. It is characterized by a poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C resulting in tendency to thrombosis. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Budd-Chiari syndrome (BDCHS) [MIM:600880]: A syndrome caused by obstruction of hepatic venous outflow involving either the hepatic veins or the terminal segment of the inferior vena cava. Obstructions are generally caused by thrombosis and lead to hepatic congestion and ischemic necrosis. Clinical manifestations observed in the majority of patients include hepatomegaly, right upper quadrant pain and abdominal ascites. Budd-Chiari syndrome is associated with a combination of disease states including primary myeloproliferative syndromes and thrombophilia due to factor V Leiden, protein C deficiency and antithrombin III deficiency. Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare but typical complication in patients with polycythemia vera. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR) [MIM:601367]: A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Pregnancy loss, recurrent, 1 (RPRGL1) [MIM:614389]: A common complication of pregnancy, resulting in spontaneous abortion before the fetus has reached viability. The term includes all miscarriages from the time of conception until 24 weeks of gestation. Recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more consecutive spontaneous abortions. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variations affecting the gene represented in this entry Similarity: Belongs to the multicopper oxidase family. Contains 3 F5/8 type A domains. Contains 2 F5/8 type C domains. Contains 6 plastocyanin-like domains. Database links: Entrez Gene: 2153 Human Omim: 612309 Human SwissProt: P12259 Human Unigene: 30054 Human Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验当FITC在碱性溶液中与抗体蛋白反应时,主要是蛋白质上赖氨酸的r氨基与荧光素的硫碳胺键(thiocarbmide)结合,形成FITC-蛋白质结合物,即荧光抗体或荧光结合物。一个IgG分子中有86个赖氨酸残基,一般最多能结合15~20个,一个IgG分子可结合2~8个分子的FITC,其反应式如下FITC-N=C=S + N-H2-蛋白质 → FITC-NS-C-N-H2-蛋白质常用Marsshall(1958)法标记荧光抗体,也可以根据条件采用Chadwick等标记法或Clark
ml三蒸水中即成; 方法与步骤: 根据Marshall氏法高效价的抗人球蛋白兔免疫血清,分离球蛋白。 1. 用0.15 mol/L NaCl的盐水及0.15 mol/L pH9.0的NaHCO3-Na2CO3缓冲液稀释使每毫升内含抗体10mg,缓冲液为总量的10%; 2. 将以上溶液降温至4℃,按蛋白:荧光素=50—80mg:1mg的比例加入异硫氰酸荧光素,在0—4℃下电磁搅拌12—14h; 3.用半饱和硫酸铵将标记球蛋白
5. 过柱。取透析过夜的标记物,过葡萄糖凝胶G-25或G-50柱,分离出游离荧光素,收集标记的荧光抗体进行鉴定。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料