相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
上海联迈生物工程有限公司
- 库存:
大量
- 目录编号:
LM-5969R
- 克隆性:
多克隆
- 抗原来源:
Rabbit
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
PLAG1
- 抗体名:
多型性腺瘤基因1蛋白抗体
- 宿主:
Rabbit
- 适应物种:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse,
- 免疫原:
KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human PLAG1:21-120/500
- 亚型:
IgG
- 形态:
Lyophilized or Liquid
- 应用范围:
WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
Store at -20 °C
- 规格:
100ul 200ul
| 英文名称 | PLAG1 |
| 中文名称 | 多型性腺瘤基因1蛋白抗体 |
| 别 名 | FGFR1/PLAG1 fusion variant 3; Pleiomorphic adenoma gene 1 protein; PSA; SGPA; COL1A2/PLAG1 fusion; Plag1; PLAG1_HUMAN; Pleiomorphic adenoma gene 1; Zinc finger protein PLAG1; ZNF912. |
| 规格价格 | 100ul/1380元 购买 200ul/2200元 购买 大包装/询价 |
| 说 明 书 | 100ul 200ul |
| 研究领域 | 肿瘤 免疫学 信号转导 转录调节因子 |
| 抗体来源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆类型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反应 | Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, |
| 产品应用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 56kDa |
| 细胞定位 | 细胞核 |
| 性 状 | Lyophilized or Liquid |
| 浓 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human PLAG1:21-120/500 |
| 亚 型 | IgG |
| 纯化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 储 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存条件 | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 产品介绍 | background: Pleomorphic adenoma gene 1 encodes a zinc finger protein with 2 putative nuclear localization signals. PLAG1, which is developmentally regulated, has been shown to be consistently rearranged in pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary glands. PLAG1 is activated by the reciprocal chromosomal translocations involving 8q12 in a subset of salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] Function: Transcription factor whose activation results in up-regulation of target genes, such as IGFII, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation: when overexpressed in cultured cells, higher proliferation rate and transformation are observed. Other target genes such as CRLF1, CRABP2, CRIP2, PIGF are strongly induced in cells with PLAG1 induction. Proto-oncogene whose ectopic expression can trigger the development of pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary gland and lipoblastomas. Overexpression is associated with up-regulation of IGFII, is frequently observed in hepatoblastoma, common primary liver tumor in childhood. Cooperates with CBFB-MYH11, a fusion gene important for myeloid leukemia. Subunit: Interacts with KPNA2, which escorts protein to the nucleus via interaction with nuclear localization signal. Interacts with E3 SUMO-protein ligase PIAS1, PIAS2 and PIAS4. Subcellular Location: Nucleus. Strong nucleolar localization when sumoylation is inhibited. Tissue Specificity: Expressed in fetal tissues such as lung, liver and kidney. Not detected or weak detection in normal adult tissues, but highly expressed in salivary gland with benign or malignant pleiomorphic adenomas with or without 8q12 abberations, with preferential occurrence in benign tumors. Post-translational modifications: Sumoylated by SUMO1; which inhibits transcriptional activity, but does not affect nuclear localization. Blockers of sumoylation pathway such as SENP3 and inactive UBE2I increases transcriptional capacity. Sumoylation is increased in the presence of PIAS1. Acetylated by lysine acetyltransferase EP300; which activates transcriptional capacity. Lysine residues that are sumoylated also seem to be target for acetylation. DISEASE: Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PLAG1 is found in salivary gland pleiomorphic adenomas, the most common benign epithelial tumors of the salivary gland. Translocation t(3;8)(p21;q12) with constituvely expressed beta-catenin/CTNNB1. Fusion occurs in the 5'-regulatory regions, leading to promoter swapping between the 2 genes and activation of PLAG1 expression in adenomas. The chimeric transcript is formed by fusion of CTNNB1 exon 1 to PLAG1 exon 3. Reciprocal fusion transcript consisting of PLAG1 exon 1 and CTNNB1 exon 2-16 is also revealed in some adenomas. Translocation t(3;8)(p21;q12) with transcription elongation factor SII/TCEA1. The fusion transcript is composed of 5'-non-coding sequences as well as 63 nucleotides of the coding region of TCEA1 fused to the acceptor splice site of PLAG1 exon 3. The fusion transcript encodes a truncated TCEA1-PLAG1 protein of 90 AA as well as an apparently normal PLAG1 protein. Reciprocal fusion transcript PLAG1-TCEA1 is also present in one adenoma. Translocation t(5;8)(p13;q12) with leukemia inhibitory factor receptor LIFR. This fusion occured in the 5'-non-coding sequences of both genes, exchanging regulatory control element while preserving the coding sequences. Translocation t(6;8)(p21.3-22;q13) with Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain-containing protein 7/CHCHD7. Fusion occurs in the 5' regulatory regions, leading to promoter swapping and up-regulation of PLAG1 expression. Ectopic expression of PLAG1 under the control of promoters of distinct translocation partner genes is a general pathogenetic mechanism for pleiomorphic adenomas with 8q aberrations. These fusion genes are likely to be found in adenomas with normal karyotype as this subgroup of tumors also exhibit PLAG1 activation. Note=A chromosomal aberration involving PLAG1 may be a cause of lipoblastomas, which are benign tumors resulting from transformation of adipocytes, usually diagnosed in children. 8q12.1 to 8q24.1 intrachromosomal rearrangement with hyaluronic acid synthase 2/HAS2 results in promoter swapping and activation of PLAG1 expression. The breakpoint of HAS2 gene is in PLAG1 intron 1, whereas its coding sequence starts at exon 2 or exon 3. Translocation t(7;8)(p22;q13) with collagen 1A2/COL1A2. Fusion transcript COL1A2-PLAG1 as well as HAS2-PLAG1 encode a full-length PLAG1 protein. Similarity: Belongs to the krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family. Contains 7 C2H2-type zinc fingers. SWISS: Q6DJT9 Gene ID: 5324 Database links: Entrez Gene: 5324 Human Entrez Gene: 56711 Mouse Entrez Gene: 297804 Rat Omim: 603026 Human SwissProt: Q6DJT9 Human SwissProt: Q9QYE0 Mouse SwissProt: Q5U2T6 Rat Unigene: 14968 Human Unigene: 331467 Mouse Unigene: 39161 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
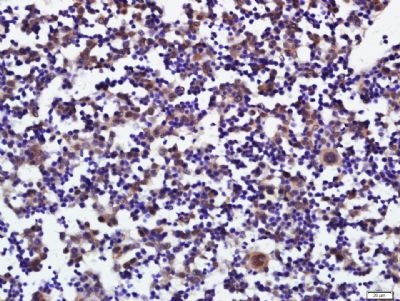
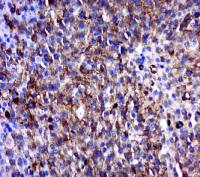
| 产品图片 | 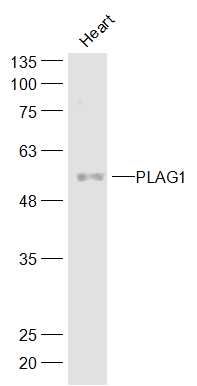 Sample: Heart(Mouse) Cell Lysate at 40 ug Primary: Anti-PLAG1 (bs-5969R) at 1/300 dilution Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution Predicted band size: 56 kD Observed band size: 56 kD 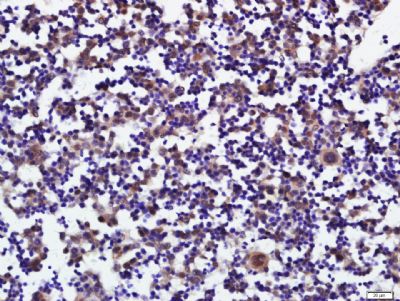 Tissue/cell: mouse embryo liver; 4% Paraformaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded; Antigen retrieval: citrate buffer ( 0.01M, pH 6.0 ), Boiling bathing for 15min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% Hydrogen peroxide for 30min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum,C-0005) at 37℃ for 20 min; Incubation: Anti-PLAG1 Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated(bs-5969R) 1:400, overnight at 4°C, followed by conjugation to the secondary antibody(SP-0023) and DAB(C-0010) staining |
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验由于免疫组化具有特异性强、灵敏度高、定位准确等特点,且能将形态研究与功能研究有机地结合在一起,所以,这门新技术已被广泛地应用于生物学和医学研究的许多领域。在病理学研究中,免疫组化技术的作用和意义更为重要。以肿瘤研究为例,在免疫组化技术出现以前,对肿瘤的诊断和分类还局限于细胞水平,而引入免疫组化技术后,则使研究的深度提高到了生物化学水平、分子水平。近年来,伴随基因探针研究而兴起的核酸分子原位杂交技术也正在蓬勃发展,更使免疫组化如虎添翼,两者相得益彰,将研究推进到了基因水平。1、确定细胞
杂交技术也正在蓬勃发展,更使免疫组化如虎添翼,两者相得益彰,将研究推进到了基因水平。 1、确定细胞类型 通过特定抗体标记出细胞内相应抗原 成分,以确定细胞类型。如角蛋白是上皮性标记,前列腺特异性抗原仅见于前列腺上皮,甲状腺球蛋白抗体是甲状腺滤泡型癌的敏感标记,而降钙素抗体是甲状腺髓样癌的特有标记。有些细胞(如表皮内朗格汉斯细胞、黑色素细胞、淋巴结内指突状和树突状网织细胞)光镜下不易辨认,但免疫组化标记(S-100蛋白等)能清楚显示其形态。 2、辨认细胞产物
肿瘤免疫细胞化学 一、细胞骨架中的中间丝蛋白 (一)神经细丝酸性蛋白 (二)神经细丝 二、神经特异性烯醇化酶 三、S-100蛋白 第二节 神经内分泌肿瘤免疫细胞化学 一、垂体腺瘤 (一)生长激素腺瘤 (二)催乳激素腺瘤 (三)促甲状腺激素腺瘤 (四)促肾上腺皮质激素腺瘤 (五)促性腺激素腺瘤 (六)多种激素性腺瘤 (七)无功能活性腺瘤 二、胰岛细胞瘤 三、甲状腺髓样癌 四、肺支气管类癌及肺小细胞癌 五、食管燕麦细胞癌 六、皮肤神经内分泌癌(Merker细胞瘤) 第三节 软组织与骨
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料