研选同类产品更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 用户评价
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 保存条件:
-20℃ to -80℃
- 保质期:
12个月
- 英文名:
Recombinant Human PD-L1 / B7-H1 / CD274 Protein (His Tag)
- 库存:
99
- 供应商:
北京义翘神州科技股份有限公司
- 规格:
1.00 mg/100.00 µg/200.00 µg
| 规格: | 1.00 mg | 产品价格: | ¥21030.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 规格: | 100.00 µg | 产品价格: | ¥3220.0 |
| 规格: | 200.00 µg | 产品价格: | ¥3870.0 |
重组人 PD-L1 / B7-H1 / CD274 蛋白 (His标签)(产品说明)
蛋白名称:Human PD-L1 / B7-H1 / CD274 Protein (His Tag)
蛋白构建:A DNA sequence encoding the N-terminal segment (Met 1-Thr 239) of the extracellular domain of human B7-H1 (NP_054862.1) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag.
表达宿主:HEK293 Cells
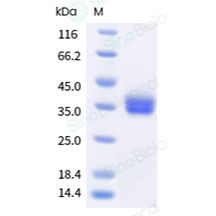
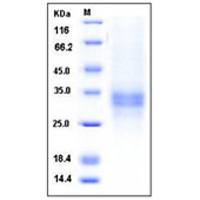
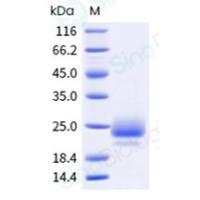
蛋白纯度:> 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE
蛋白活性:1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human B7-H1 at 20 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human PD1 with a linear range of 0.032-0.8 μg/ml. 2. Using the Octet RED System, the affinity constant (Kd) of PD-1 Protein, Human, Recombinant (Fc Tag) (Cat. 10377-H02H) bound PD-L1 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His Tag) (Cat. 10084-H08H) was 19.2nM.
蛋白内毒素:< 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method
预测N端:Phe 19
蛋白分子量:The recombinant mature human B7-H1 comprises 232 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 26.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the human B7-H1 migrates as an approximately 35-38 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
蛋白NP号:NP_054862.1
蛋白氨基酸序列:Met1-Thr239
蛋白标签:C-His
蛋白保存条件:Store it under sterile conditions at -20℃ to -80℃. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 用户评价
用户评价 暂无用户评价
暂无用户评价 文献和实验
文献和实验1, Schofield DJ, et al. Activity of murine surrogate antibodies for durvalumab and tremelimumab lacking effector function and the ability to deplete regulatory T cells in mouse models of cancer.mAbs, PubMed ID: 33397194
2, Wang F, et al. Discovery of a new inhibitor targeting PD-L1 for cancer immunotherapy.Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.), PubMed ID: 33529880
3, Xing Y, et al. New electrochemical method for programmed death-ligand 1 detection based on a paper-based microfluidic aptasensor.Bioelectrochemistry (Amsterdam, Netherlands), PubMed ID: 33677221
4, Li M, et al. Next generation of anti-PD-L1 Atezolizumab with enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in vivo.Scientific reports, PubMed ID: 33707569
5, Jeong S, et al. Novel anti-4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibody augments anti-tumor immunity through tumor-directed T-cell activation and checkpoint blockade.Journal for immunotherapy of cancer, PubMed ID: 34230109
6, Banta KL, et al. Mechanistic convergence of the TIGIT and PD-1 inhibitory pathways necessitates co-blockade to optimize anti-tumor CD8+ T cell responses.Immunity, PubMed ID: 35263569
7, He B, et al. PDL1Binder: Identifying programmed cell death ligand 1 binding peptides by incorporating next-generation phage display data and different peptide descriptors.Frontiers in microbiology, PubMed ID: 35910615
8, Yi M, et al. Anti-TGF-β/PD-L1 bispecific antibody promotes T cell infiltration and exhibits enhanced antitumor activity in triple-negative breast cancer.Journal for immunotherapy of cancer, PubMed ID: 36460337
9, Parkinson J, et al. The RESP AI model accelerates the identification of tight-binding antibodies.Nature communications, PubMed ID: 36709319
10, Wang F, et al. Identification of CBPA as a New Inhibitor of PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction.International journal of molecular sciences, PubMed ID: 36835382
11, Zhang Y, et al. Preclinical development of novel PD-L1 tracers and first-in-human study of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-RW102 in patients with lung cancers.Journal for immunotherapy of cancer, PubMed ID: 38580333
12, Yao Y, et al. Construction and preclinical evaluation of a 124I-labelled bispecific antibody targeting PD-L1 and PD-L2.European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, PubMed ID: 39155310
13, Xu X, et al. A Novel Monoclonal Antibody against PD-1 for the Treatment of Viral Oncogene-Induced Tumors or Other Cancer.Cancers, PubMed ID: 39272910
14, Mao C, et al. In situ editing of tumour cell membranes induces aggregation and capture of PD-L1 membrane proteins for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Nature communications, PubMed ID:39521768
15, Sun M, et al. Discovery of Daclatasvir as a potential PD-L1 inhibitor from drug repurposing. Bioorganic chemistry, PubMed ID:39418845
质,小分子或是金属。当融合有亲和标签的蛋白通过标签-配体作用结合再层析基质上时,通过洗杂步骤,即可去除掉其他的细胞成分。 为了洗脱所需要的蛋白质,通过改变缓冲液的条件,如pH,或通过竞争亲和标签和配体连接的方法来进行。 但怎样的纯化是较为成功的呢?仅达到所需的质量量级,如毫克级(或克级)即可满足吗? 这些并不简单。质在蛋白纯化中同样尤为重要,比如,就蛋白的生物活性和纯度而言,通常会有所要求。 以下我们来讨论并且比较2种技术: His-tag系统和Strep-tag®系统,都使用了亲和层析法来纯化
Strep-tag®技术是亲和纯化重组蛋白的常用工具,它基于自然界中最强的非共价相互作用之一,即生物素与链霉亲和素的相互作用。该纯化系统的突出特点是纯化过程温和、目的蛋白纯度高、特异性强、兼容多种表达系统,对于有挑战性蛋白的纯化十分有帮助,因此近些年来脱颖而出。 本文将从以下方面介绍Strep-tag®技术: 标签介绍 纯化原理 标签-配体 纯化步骤 系统特点 标签介绍 目前有2种广泛使用的Strep标签: 它们分别是: Strep-tag®II 8 aa小标签(Trp-Ser
IBA 第三代 Strep-tag® 高效蛋白纯化系统,由 Twin-Strep-tag® 搭配全新研发出的 Strep-Tactin®XT 组合而成。在此系统中,Strep-Tactin®XT 与 Twin-Strep-tag® 的亲和力提升至 pM 的范围,与 Strep-tag®II 的亲和力也已升至 nM 的范围。 亲和力大幅改善,其间的链结仍保有可逆性,纯化过程同样温和。仅需简单直接的再生步骤,填料即可重复利用。Strep-Tactin®XT 提升的亲和力能确保您在温和的生理纯化条件
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料