相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
100
- 供应商:
上海酶研生物科技有限公司
- 英文名:
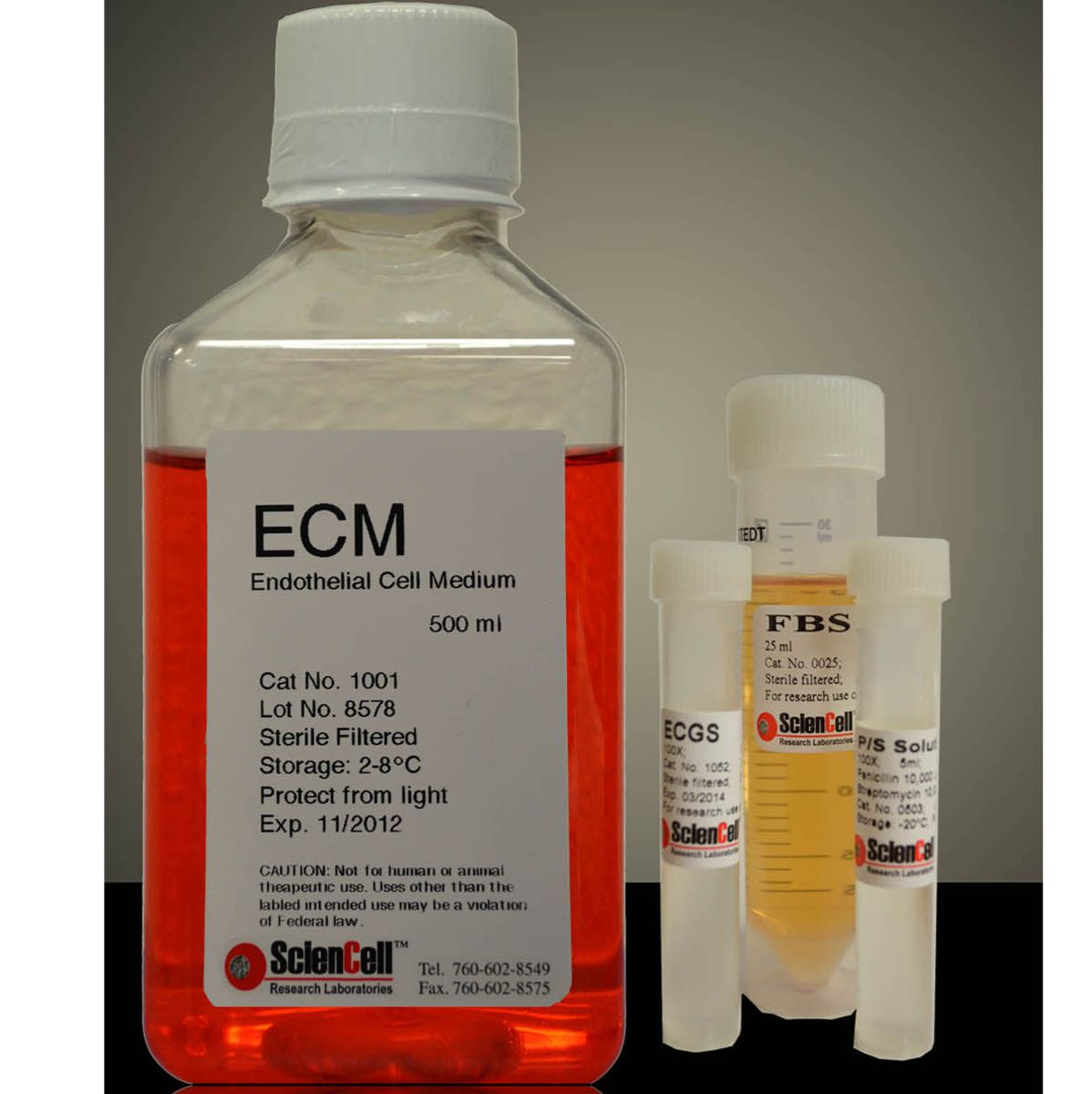
SteCM (Stellate Cell Medium)
- 规格:
500ml/T
|
货号 |
5301 |
|
产地 |
美国 |
|
缩写 |
SteCM |
|
规格 |
500ml |
|
用途 |
科研 |
|
储存 |
4度,-20度 |
|
运输 |
胶冰 |
星状细胞培养基是为正常人类肝脏星状细胞体外培养设计的适于其生长的培养基。经灭菌的液体培养基,包含必需和非必需氨基酸、维生素、有机和无机化合物、激素、生长因子、微量矿物质和低浓度胎牛血清(2%)。该培养基缓冲体系为重碳酸盐,在含5%CO2的细胞培养箱中平衡后pH值为7.4。该培养基的配方能够选择性的促进正常人类星形细胞体外培养中的增殖和生长,并为其达到理想营养平衡状态提供数量上和质量上的保证。
星状细胞培养基包含500 ml基础培养基,10ml胎牛血清(FBS,目录编号0010),5ml星状细胞生长添加物(SteCGS,目录编号5352)和5 ml青霉素/链霉素溶液(P/S,目录编号0503)
1. Sasaki, R., Kanda, T., Nakamura, M., Nakamoto, S., Haga, Y., Wu, S., Shirasawa, H. & Yokosuka, O. (2016) Possible Involvement of Hepatitis B Virus Infection of Hepatocytes in the Attenuation of Apoptosis in Hepatic Stellate Cells PLoS One. 11
Background The induction of apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is a promising therapeutic strategy against hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatic fibrosis. The underlying mechanisms of apoptosis in HSCs, however, are unknown under consideration of HBV infection. In this study, the effects of HBV on apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling in HSCs were examined. Methods The effects of conditioned media (CM) from HepG2.2.15 on apoptosis induced by the proteasome inhibitor MG132 in LX-2 and HHSteC were studied in regard to c-Jun. In combination with c-Fos, c-Jun forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor, leading to AP-1 activation, signal transduction, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and apoptosis. Results In LX-2 cells, MG132 treatment was associated with the phosphorylation of c-Jun, activation of AP-1 and apoptosis. However, in the presence of CM from HepG2.2.15, these phenomena were attenuated. In HHSteC cells, similar results were observed. HBV genomic DNA is not involved in the process of HSC apoptosis. It is possible that HBeAg has an inhibitory effect on MG132-induced apoptosis in LX-2. We also observed the upregulation of several ER stress-associated genes, such as cAMP responsive element binding protein 3-like 3, inhibin-beta A and solute carrier family 17-member 2, in the presence of CM from HepG2.2.15, or CM from PXB cells infected with HBV. Conclusions HBV inhibits the activation of c-Jun/AP-1 in HSCs, contributing to the attenuation of apoptosis and resulting in hepatic fibrosis. HBV also up-regulated several ER stress genes associated with cell growth and fibrosis. These mechanistic insights might shed new light on a treatment strategy for HBV-associated hepatic fibrosis. Less
2. Kramer, B., Finnemann, C., Sastre, B., Lutz, P., Gl?ssner, A., Wolter, F., Goeser, F., Kokordelis, P., Kaczmarek, D., Nischalke, H.D., Strassburg, C.P., Spengler, U. & Nattermann, J.(2016) 'IL28B Genetic Variants Determine the Extent of MonocyteInduced Activation of NK Cells in Hepatitis C' PLoS One. VOL 11
3. Jakubowska, M.A., Ferdek, P.E., Gerasimenko, O.V., Gerasimenko, J.V. & Petersen, O.H.(2016) 'Nitric oxide signals are interlinked with calcium signals in normal pancreatic stellate cells upon oxidative stress and inflammation' Open Biology. VOL 6
The mammalian diffuse stellate cell system comprises retinoid-storing cells capable of remarkable transformations from a quiescent to an activated myofibroblast-like phenotype. Activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) attract attention owing to the pivotal role they play in development of tissue fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. However, little is known about the actual role of PSCs in the normal pancreas. These enigmatic cells have recently been shown to respond to physiological stimuli in a manner that is markedly different from their neighbouring pancreatic acinar cells (PACs). Here, we demonstrate the capacity of PSCs to generate nitric oxide (NO), a free radical messenger mediating, for example, inflammation and vasodilatation. We show that production of cytosolic NO in PSCs is unambiguously related to cytosolic Ca2+ signals. Only stimuli that evoke Ca2+ signals in the PSCs elicit consequent NO generation. We provide fresh evidence for the striking difference between signalling pathways in PSCs and adjacent PACs, because PSCs, in contrast to PACs, generate substantial Ca2+-mediated and NOS-dependent NO signals. We also show that inhibition of NO generation protects both PSCs and PACs from necrosis. Our results highlight the interplay between Ca2+ and NO signalling pathways in cell–cell communication, and also identify a potential therapeutic target for anti-inflammatory therapies. Less
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验
1.) Wagner I,?Materne EM,?Brincker S,?S??bier U,?Fr?drich C,?Busek M,?Sonntag F,?Sakharov DA,?Trushkin EV,?Tonevitsky AG,?Lauster R,?Marx U. (2013) "A dynamic multi-organ-chip for long-term cultivation and substance testing proven by 3D human liver and skin tissue co-culture." Lab Chip. doi: 10.1039/c3lc50234a
为了在玻璃器内培养细胞、组织、器官或微生物和某些昆虫等,需要配制营养物质,并加入这种为培养所需的营养物质的混合物,为培养基。从生物生存发育所不可缺少的水开始,至少要求有生物体构成成分的 C、 H、 O、 N、 P、 S、 K、 Ca、 Mg、 Mn、 Fe等各种营养元素,这里除一部分可从气体中得到外,其他所有无机或有机化合物,需要从培养基中获得。需要何种化合物,要依生物的营养型,例如自养的,异养或寄生的而定。一般从营养来源因素来看,可以区分为炭源、氮源、无机盐类、发育因子等。营养物是从
HAT系次黄嘌呤( hypoxantin)、氨基蝶呤( aminopterin)和胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷( thymidin)三种物质各英文首字之缀列, HAT培养基也就是指含有这三种物质的细胞培养基。对具有合成 DNA原料的核苷酸的形成上,在细胞内具有起始合成途径( de novo pathway)和中间合成途径( salvage pa-thway)。由于氨基蝶呤可阻碍起始合成途径,所以培养基中含有它时,细胞便只有中间合成途径,所以必须供给核苷酸。至于缺失中间合成途径的细胞,可失去增殖能力臻
培养动物细胞时,有时不用新调制的培养液,而是用已培养过多数细胞的培养液,这种培养液被认为是已由培养细胞进行了某些调整故称之为调整培养基。培养极少数细胞时,常常只有通过使用这种培养液才有可能使细胞增殖。从调整培养基中,还未单独分离出有效因子。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料