相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 保质期:
1年
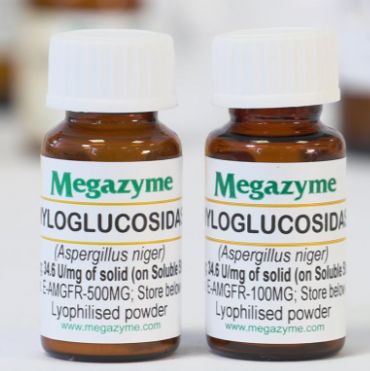
- 英文名:
Amyloglucosidase (A. niger)
- 库存:
请咨询
- 供应商:
上海经科化学科技有限公司
- 保存条件:
-20℃
- 规格:
100mg/500mg
| 规格: | 100mg | 产品价格: | ¥3325.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 规格: | 500mg | 产品价格: | ¥9303.0 |
High purity Amyloglucosidase (Asper-gillus niger) for use in research, biochemical enzyme assays and in vitro diagnostic analysis.
Amyloglucosidase and fructanase (E-FRMXLQ) are used in the enzyme hydrolysis step of the AOAC method 997.08 for the determination of fructan in foods.
| Content: | 500 mg or 100 mg |
| Shipping Temperature: | Ambient |
| Storage Temperature: | Below -10oC |
| Formulation: | Supplied as a lyophilised powder |
| Physical Form: | Powder |
| Stability: | > 1 year under recommended storage conditions |
| Enzyme Activity: | Amyloglucosidase |
| EC Number: | 3.2.1.3 |
| CAZy Family: | GH15 |
| CAS Number: | 9032-08-0 |
| Synonyms: | glucan 1,4-alpha-glucosidase; 4-alpha-D-glucan glucohydrolase; glucoamylase |
| Source: | Asper-gillus niger |
| Molecular Weight: | 143,500 |
| Expression: | From Asper-gillus niger |
| Specificity: | Hydrolysis of terminal α-1,4 and α-1,6 D-glucose residues successively from non-reducing ends of maltodextrins. |
| Specific Activity: | ~ 35 U/mg (40oC, pH 4.5 on soluble starch) |
| Unit Definition: | One Unit of amyloglucosidase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release one µmole of D-glucose reducing-sugar equivalents per minute from soluble starch at pH 4.5 and 40oC. |
| Temperature Optima: | 70oC |
| pH Optima: | 4 |
| Application examples: | Recommended for use in AOAC Method 997.08 (fructan). |
| Method recognition: | AOAC Method 997.08, AOAC Method 997.08, AOAC Method 2000.11 and GB Standard 5009.245-2016 |
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验1.Relationship between the digestion rate and internal fatty acid content of starch rendered resistant by addition of fatty acids and heat treatment.
Nakashima, K., Oki, S., Toyoshima, R., Tozawa, S., Nakayama, M., Ishikawa, K., Zhang, H., Chen, J., Mori, D. & Akiyama, Y. (2018). Japan Journal of Food Engineering, 19(3), 185-189.
Shrestha, A. K., Ng, C. S., Lopez-Rubio, A., Blazek, J., Gilbert, E. P. & Gidley, M. J. (2010). Carbohydrate Polymers, 80(3), 699-710.
指以有机物而不是以二氧化碳作为主要碳源或唯一碳源,以无机或有机氮化物作为氮源进行生长的生物。一般需要供给外源生长因子。自然界中绝大多数生物均属异养型,包括人类、动物、少数植物和极大多数微生物,如真菌、放线菌、大多数细菌等。有机碳化物对这些生物来说,既是碳源,也是能源,它们不仅利用有机物合成机体内的含碳化合物,并且通过氧化有机物获得生长所需要的能量。在异养型微生物中,包括两大类,一类是摄取无生命的有机物,称为腐生。如黑曲霉( Aspergillus niger)、黑根霉
指以有机物而不是以二氧化碳作为主要碳源或唯一碳源,以无机或有机氮化物作为氮源进行生长的生物。一般需要供给外源生长因子。自然界中绝大多数生物均属异养型,包括人类、动物、少数植物和极大多数微生物,如真菌、放线菌、大多数细菌等。有机碳化物对这些生物来说,既是碳源,也是能源,它们不仅利用有机物合成机体内的含碳化合物,并且通过氧化有机物获得生长所需要的能量。在异养型微生物中,包括两大类,一类是摄取无生命的有机物,称为腐生。如黑曲霉( Aspergillus niger)、黑根霉( Rhi
DNA 转化 Chemical Transformation ・ Transformation of Competent Cells (RbCl2 Method) (Goldberg Lab) Very nice protocol for E. Coli transformation including competent cell preparation and recipes ・




![纤维素酶[1,4-D-葡聚糖内切酶[黑曲菌] E-CELAN Cellulase (endo-1,4-β-D-glucanase) (Asper-gillus niger)](https://img1.dxycdn.com/p/s14/2024/0811/849/2171183549872362281.jpg!wh200)



