Approaches to the Identification of ABAR as an Abscisic Acid Receptor
互联网
404
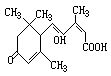
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a vital phytohormone that regulates seed maturation and germination, seedling growth, and adaptation to environmental stresses. ABA functions through a complex network of signaling pathways, where the cell response is initiated by an ABA receptor which triggers downstream signaling cascades to induce the final physiological effects. Two classes of technologies may be used for the isolation of ABA receptors. One is the genetic screening for ABA receptor mutants, and another is the biochemical isolation of ABA-binding proteins that are putative ABA receptors. We implemented biochemical approaches, namely, the purification of ABA-binding proteins to identify a putative ABA receptor; this protein was further characterized by a combination of biochemical and reverse genetic approaches. The identified ABA receptor, called ABAR, mediates the responses of plants to ABA in seed germination, postgerminative growth, and stomatal movement. This protein is the H subunit (CHLH) of the magnesium protoporphyrin-IX chelatase (Mg-chelatase) that also plays a key role in both chlorophyll biosynthesis and plastid-to-nucleus signaling. Here, we describe the experimental procedures for the purification of ABA-binding proteins and the identification of the ABA-binding protein, ABAR/CHLH, as an ABA receptor.


![DKFZ-PSMA-11,4,6,12,19-Tetraazadocosane-1,3,7-tricarboxylic acid, 22-[3-[[[2-[[[5-(2-carboxyethyl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]methyl](carboxymethyl)amin](https://img1.dxycdn.com/p/s14/2025/1009/171/0405943971658126791.jpg!wh200)