Laser Speckle Imaging
互联网
948
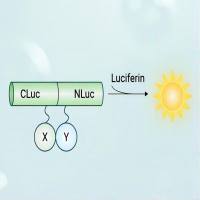
Impaired cortical cerebral blood flow (CBF) is a main indicator for hemodynamic perfusion deficits of the brain. After aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), vasospasm may cause hemodynamic hypoperfusion and subsequent cortical border zone infarction. In order to provide dynamic real-time assessment of cortical CBF after experimental SAH, Laser Speckle Contrast Analysis (LASCA) serves as a novel tool for semiquantitative and noninvasive cortical perfusion measurement with high spatial and temporal resolution. This chapter describes the principle of LASCA, technique and procedure, pitfalls and limitations of the technique on the basis of a mouse model of aneurysmal SAH.