Use of B-PER lysis reagent to purify recombinant proteins tagged with His6 or maltose binding protein
互联网
George P.Smith
Division of Biological Sciences
Tucker Hall
(573)882-3344
Introduction to B-PER
B-PER from Pierce Chemical Co.is a Tris-buffered detergent formulation that lyses bacterial cells without denaturing enzymes or other bioactive proteins.It is a convenient alternative to sonication for extracting recombinant proteins from the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli cells carrying expression vectors,especially when many proteins are to be processed in parallel.
In this article I’ll summarize our extensive experience with B-PER for isolating fusion proteins in which the fusion partner is either IPIII-His (an internal protein of bacteriophage T4 with a His tag at the C-terminus)or MBP (the E.coli maltose binding protein).The two cases illustrate two types of post-lysis processing.On the one hand,His-tagged proteins can be purified on nickel affinity columns under fully denaturing conditions and renatured while still tethered to the column matrix; this aids renaturation by promoting intra-molecular folding at the expense of inter-molecular aggregation.On the other hand,MBP-tagged proteins must acquire and retain their native conformation in order to be purified on amylose affinity columns.Presumably the methods below can be adapted with few changes to other types of fusion proteins.
Expression of the fusion proteins
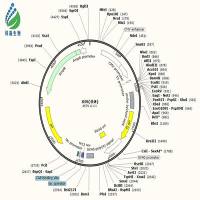
Structures of the plasmid constructs encoding the IPIII-His and MBP fusion proteins are diagrammed in the figure; in both cases,the vector backbone is pET 29a(+)(Novagen Inc.,Madison,WI; shaded portions in the figure),so that the fusion proteins are expressed from a T7 promoter upon induction with isopropylthio--D-galactoside (IPTG).E.coli strain BL21(DE3)cells (Novagen)carrying the fusion plasmids were inoculated into 300 ml (IPIII-His fusions)or 900 ml (MBP fusions)LB medium (Sambrook et al.,1989)containing kanamycin at 50 µg/ml (the plasmid vector confers resistance to this drug).The cultures were shaken vigorously at 37ºC until the optical density at 600 nm reached 0.5; IPTG was then added to a final concentration of 1 mM and shaking continued for an additional 90 min.Cultures were chilled and centrifuged to pellet the cells,the supernatants were discarded,the bottles were re-centrifuged,all residual supernatants were aspirated,and the cell pellets were frozen and stored at –80ºC.
Lysis
Lysis was accomplished with B-PER reagent supplemented with 1/50 vol 10-mg/ml chicken egg-white lysozyme (stored at –80ºC in aliquots),1/125 vol 5-mg/ml DNaseI (in 20 mM sodium acetate,pH adjusted to 6.5 with NaOH,5 mM CaCl2,50% glycerol; stored at –20ºC),and 1/100 vol 1 M MgCl2.Lysozyme enhances lysis by degrading the peptidyl glycan cell wall; DNaseI enhances lysis by degrading DNA released from already-lysed cells,thereby reducing viscosity.The IPIII-His fusion pellets (from 300-ml cultures)were thawed and suspended in 7.5 ml of this mixture; the MBP fusion pellets (from 900-ml cultures)were thawed and suspended in 20 ml.The suspensions were shaken fairly vigorously for 10 min at room temperature,by which time the pellets were uniformly dispersed in the lysis solution.From this point,the IPIII-His and MBP fusion lysates were processed differently,as detailed in the next two paragraphs.
Purification of His-tagged fusion proteins
To each IPIII-His fusion lysate was added 10 g guanidinium chloride (GuHCl); after multiple inversions to dissolve the solid and 5 min of shaking,the solutions were centrifuged at 15,000 rev/min in the Sorvall SS34 rotor for 10 min at 4ºC.The supernatants were passed through 1-ml nickel affinity columns (B-PER 6×His fusion protein purification kit from Pierce)that had been pre-equilibrated with 7 M GuHCl in TBS (0.15 M NaCl,50 mM Tris.HCl pH 7.5).The columns were washed thrice with 1 ml 7 M GuHCl; once each with 1.4 ml 6,5,4,3,2 and 1 M GuHCl; once with 3 ml TBS; thrice with 3 ml Wash Buffer 1 and thrice with 3 ml Wash Buffer 2 (both wash buffers from the above-mentioned Pierce kit); all the GuHCl solutions were made up in TBS.The His-tagged fusion proteins were eluted with two 3-ml portions of elution buffer (Pierce kit); diluted to 13 ml with TBS; dialyzed at 4ºC against two changes of TBS and three changes of PBS (0.15 M NaCl,5 mM NaH2PO4,pH adjusted to 7.0 with NaOH); and stored at –20ºC.Protein concentration was measured spectrophotometrically in 6 M GuHCl (Edelhoch,1967); final yields were 10–18 mg.
Purification of MBP-tagged fusion proteins
The MBP fusion lysates were diluted with 85 ml cold amylose column buffer (0.2 M NaCl,20 mM NaH2PO4,1 mM Na2EDTA,pH 7.2)and centrifuged at 14,000 rev/min in high-speed 250-ml centrifuge bottles (Nalge 3141-0250)in the Sorvall SLA-1500 rotor (with Nalge DS3125 adaptors)for 10 min at 4ºC.The supernatants were passed through 5-ml column beds of amylose resin (New England Biolabs,Inc.,Beverly,MA),which were subsequently washed with 105 ml of the same buffer and eluted with ten 2-ml portions of elution buffer (10 mM maltose in column buffer).The affinity-purified fusion proteins emerged in fractions 2–5 (measured by mixing 1-µl portions with 250 µl Pierce Coomassie protein assay reagent in 96-well ELISA dishes and reading at 650 nm on a plate reader).The foregoing affinity purification steps were carried out at 4ºC.The proteins were dialyzed against PBS and stored at –20ºC.Protein concentration was measured spectrophotometrically in 6 M GuHCl (Edelhoch,1967); final yields were 15–100 mg.
REFERENCES
Edelhoch,H.(1967).Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins.Biochemistry 6,1948–1954.
Sambrook,J.,Fritsch,E.F.,and Maniatis,T.(1989).Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual,2nd Edition (Cold Spring Harbor,N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory).