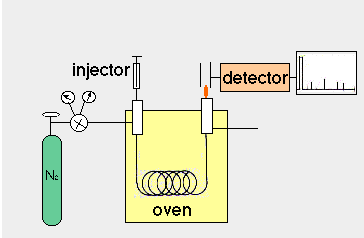
Analysis of Fatty Acids by Gas Liquid Chromatography
互联网
|
Common name |
Synonym a |
Abbreviation b |
|---|---|---|
|
Myristic |
Tetradecanoic |
14:0 |
|
Palmitic |
Hexadecanoic |
16:0 |
|
Stearic |
Octadecanoic |
18:0 |
|
Arachidic |
Eicosanoic |
20:0 |
|
Behenic |
Docosanoic |
22:0 |
|
Lignoceric |
Tetracosanoic |
24:0 |
|
Cerotic |
Hexacosanoic |
26:0 |
|
Palmitoleic |
7-Hexadecenoic |
16:1 n-9 |
|
Oleic |
9-Octadecenoic |
18:1 n-9 |
|
Gadoleic |
11-Eicosenoic |
20:1 n-9 |
|
Erucic |
13-Docosenoic |
22:1 n-9 |
|
Nervonic |
15-Tetracosenoic |
24:1 n-9 |
|
Linoleic |
9,12-Octadecadienoic |
18:2 n-6 |
|
Alpha-linolenic |
9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic |
18:3 n-3 |
|
Gamma-linolenic |
6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic |
18:3 n-6 |
|
Arachidonic |
5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic |
20:4 n-6 |
|
Adrenic |
7,10,13,16-Docosatetraenoic |
22:4 n-6 |
|
Timnodonic |
5,8,11,14,17-Eicosapentaenoic |
20:5 n-3 |
|
Clupanodonic |
4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic |
22:6 n-3 |
|
a Double bonds numbered from the carboxyl end of the molecule. |