Explant Culture of Mouse Embryonic Whole Lung, Isolated Epithelium, or Mesenchyme Under Chemically Defined Conditions as a System to Evaluate the Mole
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

JC-1,47729-63-5,A cationic, fluorescent, carbocyanine dye that can be used as a ratiometric indicator of mitochondrial potential δΨm in cells, tissues, and isolated mitochondria.,阿拉丁
¥3987.90
血清替代物II(Cell Culture Supplement)
¥2580

Aquivion® E98-15S,1163733-25-2,膜片, 已加稳定剂 CF₃ 聚合物链末端, PFSA eq. wt. 980 g/mole SO₃H, L×W×厚度 18cm×18cm×150μm,阿拉丁
¥2211.90
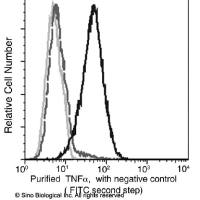
TNF-alpha / TNFA / TNFSF2 Antibody, Mouse MAb | TNF-alpha / TNFA / TNFSF2 鼠单抗
¥800

btuC/btuC蛋白/btuC; OE_2952FCobalamin import system permease protein BtuC蛋白/Recombinant Halobacterium salinarum Cobalamin import system permease protein BtuC (btuC)重组蛋白
¥69
相关问答

