Characterization of ProteinMembrane Binding Interactions via a Microplate Assay Employing Whole Liposome Immobilization
互联网
383
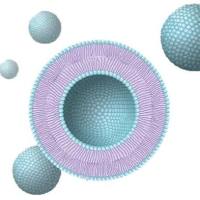
Protein–cell membrane binding interactions control numerous vital biological processes, many of which can go awry during disease onset. However, the study of these events is complicated by the complexity of the membrane bilayer. These efforts would benefit from a rapid and easily accessible method for characteri�zing protein–membrane recognition events. Herein, we describe a microplate-based method for the detection of protein–membrane binding that employs whole liposome immobilization using a biotin anchor. First, control studies are detailed to test for nonspecific liposome immobilization (fluorescence assay; see Subheading 3.2), and to ensure that liposomes remain intact on the microplate surface (dye leakage assay; see Subheading 3.3). Finally, a protein–membrane binding detection assay is described through the example of protein kinase Cα binding to surface-immobilized whole liposomes (see Subheading 3.4).