Identification of Mutations in mtDNA from Patients Suffering Mitochondrial Diseases
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

重组人 LGR5 蛋白 (stabilizing mutations, His Tag)
¥4520
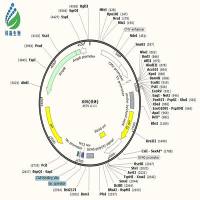
pUC57-B6mtDNA(mouse)质粒载体
¥680

Recombinant-Drosophila-melanogaster-Phosphatidylinositide-phosphatase-SAC1Sac1Phosphatidylinositide phosphatase SAC1 EC= 3.1.3.- Alternative name(s): Suppressor of actin mutations 1-like protein
¥14042

Recombinant-Bovine-Phosphatidylinositide-phosphatase-SAC1SACM1LPhosphatidylinositide phosphatase SAC1 EC= 3.1.3.- Alternative name(s): Suppressor of actin mutations 1-like protein
¥14000

Recombinant-Mouse-Phosphatidylinositide-phosphatase-SAC1Sacm1lPhosphatidylinositide phosphatase SAC1 EC= 3.1.3.- Alternative name(s): Suppressor of actin mutations 1-like protein
¥14000
相关问答

