Culture Models for the Study of Amino Acid Transport and Metabolism
互联网
648
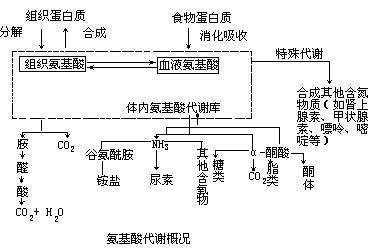
Glutamine (Gln) plays an important role in satisfying brain metabolic demands and as a precursor for the synthesis of glutamate
and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In vitro cultured cell studies have shown that carrier-mediated Gln transport between astrocytes
and neurons represents a key factor in the glutamate–GABA–glutamine cycle. Gln transport in astrocytes involves the following
systems: sodium-dependent: system N; system ASC; system A and sodium-independent: system L, whereas in neurons only systems
A and L are active. Gln-specific carriers primarily mediate not only inward transport, but can also largely contribute to
outwardly transport. Therefore, both uptake and release studies are important for the investigation of Gln transport and metabolism.
In this unit, methods are presented for radiolabel Gln uptake and efflux experiments in primary astrocyte cultures. These
methods can be useful for the investigation of Gln transport by different systems in any tested conditions. We also review
here the basic properties of the glutamate–GABA–glutamine cycle, including aspects of transport and metabolism. Furthermore,
a section is devoted to the characteristics of the transport systems N, ASC, A and L and to the functional and molecular identifications
of the Gln-specific carriers.




![DKFZ-PSMA-11,4,6,12,19-Tetraazadocosane-1,3,7-tricarboxylic acid, 22-[3-[[[2-[[[5-(2-carboxyethyl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]methyl](carboxymethyl)amin](https://img1.dxycdn.com/p/s14/2025/1009/171/0405943971658126791.jpg!wh200)