Inducible raptor and rictor Knockout Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Raptor 多克隆抗体 20984-1-AP
¥1350
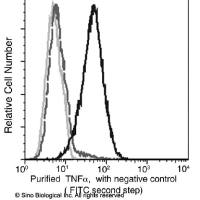
TNF-alpha / TNFA / TNFSF2 Antibody, Mouse MAb | TNF-alpha / TNFA / TNFSF2 鼠单抗
¥800

Recombinant Human RICTOR/人源RICTOR蛋白
¥2450

Recombinant-Dog-C-X-C-chemokine-receptor-type-3CXCR3C-X-C chemokine receptor type 3; CXC-R3; CXCR-3 Alternative name(s): Interferon-inducible protein 10 receptor; IP-10 receptor CD_antigen= CD183
¥12026

Recombinant-Human-Zinc-transporter-9SLC30A9Zinc transporter 9; ZnT-9 Alternative name(s): Human embryonic lung protein; HuEL Solute carrier family 30 member 9
¥13832
相关问答

