Split Gaussia Luciferase for Imaging LigandReceptor Binding
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Mannan Binding Lectin/MBL2 兔多克隆抗体
¥1699
Streptavidin-conjugated Gaussia princeps Luciferase
¥4875

AES/AES蛋白Recombinant Human Amino-terminal enhancer of split (AES)重组蛋白Gp130-associated protein GAM Grg-5 Groucho-related protein 5 Protein ESP1 Protein GRG蛋白
¥1344
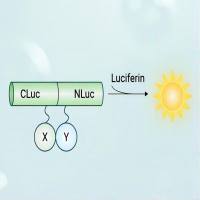
荧火素酶互补实验(Luciferase Complementation Assay, LCA)| 荧光素酶互补成像技术(Luciferase Complementation Imaging, LCI)
¥5999

Cortisol Binding Globulin/CBG重组蛋白|Recombinant Mouse Cortisol Binding Globulin Protein(AVI&His Tag),Biotinylated
¥3870
相关问答

