Noninvasive Bioluminescent Imaging of Infections
互联网
622
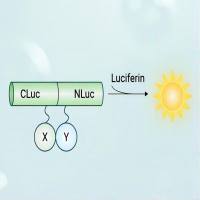
Traditional studies of viral and bacterial infection and pathogenesis have generally relied on animal models that require the sacrifice of infected animals to determine viral or bacterial distributions and titers. The recent application of the in vivo bioluminescence imaging (BLI) to monitor the replication and tropism of pathogens expressing the luciferase (from firefly or Renilla ) reporter proteins has been recently developed. This technology do not requires the sacrifice of the experimental animals, where the in vivo bioluminescence emissions in living animals permit the tracking of the infection. It has been demonstrated that the in vivo BLI is comparable to the classical approaches as measurements of in vitro light emission in organs of sacrificed animals. Moreover, molecular techniques such as PCR determinations show parallel results in pathogen quantification, where the concentrations of microbial DNA measured correlated with the magnitude of bioluminescence in vivo, and with the photon flux determined by the in vitro luciferase enzyme assay. These results show that BLI can be used for noninvasive, real-time monitoring of several infections of pathogens in living animals, supplying a new methodology in the study of pathogens in addition to conventional techniques for the characterization of infections.