Crosslinking of Proteins to mtDNA
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

yscM/yscM蛋白/yscM; Yop proteins translocation protein M蛋白/Recombinant Yersinia enterocolitica Yop proteins translocation protein M (yscM)重组蛋白
¥69
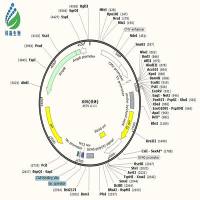
pUC57-B6mtDNA(mouse)质粒载体
¥680

///蛋白/Proteins P-6/P-7蛋白/Recombinant Chlamydia trachomatis Virulence plasmid protein pGP3-D重组蛋白
¥69

Recombinant-Human-Post-GPI-attachment-to-proteins-factor-3PGAP3Post-GPI attachment to proteins factor 3 Alternative name(s): COS16 homolog; hCOS16 Gene coamplified with ERBB2 protein PER1-like domain-containing protein 1
¥11452

Recombinant-Yop-proteins-translocation-protein-TyscTYop proteins translocation protein T
¥11102
相关问答

