抗体应用
Adoptive therapy with allogeneic or tumor-specific T-cells has shown substantial clinical effects for several human tumors, but the widespread application of this strategy remains a daunting task. The antigen specificity of T-lymphocytes is solely determined by the T-cell recept ...
In the past years a number of target antigens recognized by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) have been identified in human malignancies. In most cases, the CTL-recognized antigens did not arise from mutations, but were instead encoded by genes that were identical in normal and tumor cells. Gene ex ...
Reprogramming T-cell populations by T-cell receptor (TCR) gene transfer is a new therapeutic tool for adoptive tumor immunotherapy. Gene transfer of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-transgenic mice-derived TCR into human T-cells allows the circumvention of tolerance to tumor-ass ...
A major objective of immune analysis in the setting of cancer, cancer vaccination, and therapy is to accurately characterize and isolate functional T-cells elicited by a tumor. Secretion of cytokines is an important function of activated effector and memory T-cells. The cytokine secreti ...
The generation of an antigen-specific T-lymphocyte response is a complex multi-step process. Upon T-cell receptor-mediated recognition of antigen presented by activated dendritic cells, naive T-lymphocytes enter a program of proliferation and differentiation, during the c ...
Dendritic cells (DC) are important antigen-presenting cells (APC) that can prime naive T-cells and control lymphocyte-mediated adaptive immune responses with respect to magnitude, memory, and self-tolerance. Understanding the biology of these cells is central to the developme ...
Naturally occurring CD4+CD25+T regulatory cells originate from the thymus and play a central role regarding the maintenance of peripheral tolerance by suppression of autoreactive T-cell populations. However, T regulatory cells can have beneficial as well as harmful effects. On the o ...
Monoclonal antibodies are homogeneous sets of immunoglobulins with well-defined specificity and biochemical characteristics. They were introduced into clinical practice in the early 1980s, and since then their use has rapidly expanded. Most of the side effects observed with fir ...
Bispecific antibodies are artificially engineered monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that consist of two distinct binding sites and are capable of binding two different antigens noncovalently. They can be produced by chemical cross-linkage, genetic engineering, or somatic hybri ...
Thymocyte development is characterized by the stage-specific expression of CD4 and CD8 surface molecules (1). The earliest thymic immigrants, arriving from the fetal liver or bone marrow, lack CD4 and CD8 expression (CD4− CD8−, double negative (DN) (2). This population can be further subdiv ...
Most T lymphocytes of the immune system differentiate within the thymus along the CD4/CD8 developmental pathway by a highly ordered process termed thymic selection (1,2). The maturation status of thymocytes is commonly assessed by their expression of the coreceptor proteins CD4 and CD8 a ...
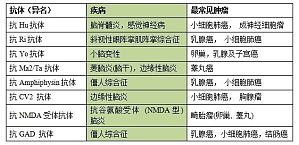
概要中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的很多疾病与抗神经元自身抗体相关,相应的靶抗原包括神经元胞内神经肿瘤抗原和神经元表面抗原。临床上,检测血清或者脑脊液中的这类自身抗体对于疾病诊断具有重要意义。抗神经肿瘤抗原的自身抗体与不同恶性肿瘤存在一定的对应关系,其实验室检验结果可以为临床医生探查肿瘤提供指导和依据。一系列针对神经元表面抗原的自身抗体阳性发生率高于已知的抗神经元胞内抗原的自身抗体。据国外临床经验显示,全面检 ...
One of the areas in which the use of immunocytochemistry has had the greatest impact is in the examination of tissue in the medical pathology laboratory. Immunocytochemistry or actually immunohistochemistry in the pathology laboratory enhances the study of diseased tissue. It is impor ...
In research, a technique that has evolved in importance is the analysis of the living cell as seen in cell culture. It is within the special boundaries of cell culture that conditions can be manipulated in order to examine living cells and to understand better their behavior (1). The fact that transform ...
Immunocytochemistry can be a valuable tool for the determination of cellular contents from individual cell suspensions. Samples that can be analyzed include blood smears, aspirates, and swabs from any cellular site. Each sample is treated differently, and yet all the methods are interc ...
Often, depending on the circumstances, it is necessary to obtain information about a lesion immediately, or the need to examine the cells without cutting into them precludes the use of frozen sections. Touch preparations or imprints enable the examination of the whole cell apart from the tissue ...
Fresh tissue must be preserved in some manner before analysis, because the substances to be tested in the tissue are often labile and cannot withstand analytical procedures without first being preserved. The best method for antigen preservation in immunocytochemical analysis is free ...
The localization of proteins and carbohydrates within cells and tissues with specific antibodies has long been proven to be a valuable technique. Immunolocalization procedures allow one not only to detect well-characterized cellular structures but also to provide information a ...
The high affinity and specificity of the avidin-biotin interaction permit diverse applications in immunology, histochemistry, in situ hybridizations, affinity chromatography, and many other areas (1) (see Chapter 21 and Chapter 22). It was first exploited in immunocytochemical ...
The use of specific antibodies labeled with a fluorescent dye to localize substances in tissues was first devised by A. H. Coons and his associates. At first, the specific antibody itself was labeled and applied to the tissue section to identify the antigenic sites (direct method) (1). Later, the more s ...