影像系统
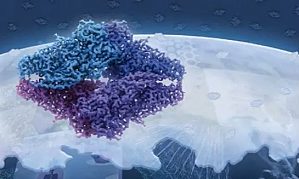
导语:每年的岁末年初,《自然》杂志旗下子刊《自然·方法》(Nature Methods)都会盘点当年的年度科学技术。2015 年最受关注的技术为冷冻电镜技术(cryo-EM),此前呼声很高的 CRISPR/Cas9 基因编辑技术未能折桂。在冷冻电镜的这场技术革命中,华人科学家功不可没,在某些方面甚至独领风骚,做出了诸多重大成果。文 | 张凯(剑桥大学 MRC 分子生物学实验室博士)细胞里面的生命活动井然有序,每一个部分都有其特定的结构,承担不同的功能。 ...
近几年光遗传学在电生理领域非常火热,在不了解它之前相信很多人会觉得很高端,很难懂。在我们了解之后会发现其实它很简单,只是一种工具的应用:通过基因工程,科学家构建出了携带有特定种类视蛋白基因的病毒载体,用它们感染培育好的实验动物,再通过各种操作将视蛋白特异性表达在某一类神经细胞上。这样一来,一类新的转基因实验动物诞生了,它们脑内将有且仅有这一类神经细胞对光敏感。视蛋白是一种对光敏感的独特蛋白,也就是附着于细胞膜 ...
正电子发射断层扫描显像(PET)是继 CT 和 MRI 影像技术后在生物医学工程领域出现的全新尖端科技,专门用于人体或动物在分子水平上的新陈代谢的功能成像。它可以在无创伤情况下进行功能、代谢和生理显像的早期诊断技术也被称为分子影像。它集材料学、核物理、放射化学、计算机技术、医学影像技术和分子生物学技术之大成被誉为二十一世纪医疗设备的高科技之冠。它是当前医学界公认最先进的大型医疗诊断成像设备,可广泛应用于肿瘤学、神经学、心血管、 ...
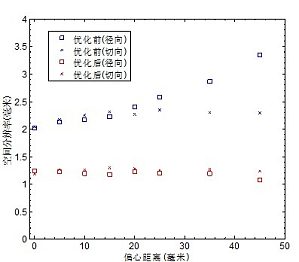
计算机断层成像技术(CT,Computed Tomography)作为一种无损成像技术,借助于 X 射线显微光学和 X 射线断层重构技术,可以在无创伤情况下提供被扫描对象的内部结构图像,其在临床医学上的应用是 20 世纪以来医疗技术进步的重要标志之一。而小动物模型在生物医学研究中有极为重要的地位,小动物、尤其是小型啮齿动物,已经成为生物和医学研究实验室用来建立人类疾病模型或者测试新药和治疗方法的动物选择。CT 技术在小动物成像中的应用,提供 ...
摘要:早期检测和随后的手术完全切除是治疗癌症最有效的方法 , 然 而检测灵敏度低和不能完全确定肿瘤边缘部位是治疗时面临的两个挑战性的问题,基于纳米颗粒的影像引导手术治疗已被证明是肿瘤靶向成像和随后的减瘤手术的有 效方法,近红外荧光探针,如近红外量子点具有深层组织渗透性和较高的灵敏度可用于肿瘤检测。本研究中,合成的近红外发光 CdTe 量子点(最大荧光发射峰为 728nm )具有 38% 的高量子产率,将环 RGD 多肽(环精氨酸 - 甘氨酸 - 天冬氨酸肽)偶联到量子点 ...
In the last two decades, fluorescent proteins became an indispensable tool to noninvasively label a protein in living cells. The discovery of photoswitchable fluorescent proteins expanded the applications of the fluorescent proteins to techniques such as molecular tracking and h ...
Single-molecule fluorescence studies of nucleic acids are revolutionizing our understanding of fundamental cellular processes related to DNA and RNA processing mechanisms. Detailed molecular insights into DNA repair, replication, transcription, and RNA folding and fun ...
In modern fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy, the autocorrelation function and photon counting distribution are two widely used statistical characteristics of the measured fluctuating fluorescence intensity signal. Applying special analysis methods such as flu ...
In fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) and photon counting histogram (PCH) analysis, the same experimental fluorescence intensity fluctuations are used, but each analytical method focuses on a different property of the signal. The time-dependent decay of the correlat ...
This chapter presents an overview of quantitative fluorescence brightness experiments with special emphasis on single-color measurements of protein homo-interactions inside living cells. We discuss practical considerations in the choice of the fluorescent labels and the ...
Dual-color FCS is a powerful method to monitor protein–protein interactions in living cells. The main idea is based on the cross-correlation analysis of temporal fluorescence intensity fluctuations of two fluorescent proteins to obtain their co-diffusion and relative concentr ...
Pulsed interleaved excitation (PIE) employs pulsed laser sources that are interleaved such that differentially colored fluorophores can be measured or imaged quasi-simultaneously in the absence of spectral crosstalk. PIE improves the robustness and reduces data analysis co ...
Scanning fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (SFCS) with a scan path perpendicular to the membrane plane was introduced to measure diffusion and interactions of fluorescent components in free-standing biomembranes. Using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM), the ...
Studies of lateral diffusion are used for the characterization of the dynamics of biological membranes. One of the techniques that can be used for this purpose is fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS), which belongs to the single-molecule techniques. Unfortunately, FCS measu ...
Quenching of organic fluorophores by aromatic amino acids and DNA nucleotides with expelled electron donating properties allows the study of conformational dynamics of biomolecules. Efficient fluorescence quenching via photoinduced electron transfer (PET) requires van ...
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a powerful method to investigate molecular interactions based on the variation of diffusion properties at the single-molecule level. This technique allows studying quantitatively the interaction of fluorescently labeled ...
Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS) is a single-molecule sensitive technique to quantitatively study interactions among fluorescently tagged biomolecules. Besides the initial implementation as dual-color FCCS (DC-FCCS), FCCS has several powerful d ...
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) can add dynamic molecular information to images of live cells. For example, a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) equipped with an accessory FCS unit provides the possibility to first image the spatial distribution of a fluorescent ...
Multimodal fluorescence imaging is a versatile method that has a wide application range from biological studies to materials science. Typical observables in multimodal fluorescence imaging are intensity, lifetime, excitation, and emission spectra which are recorded at chosen ...
Fluorescence can be characterized by its intensity, position, wavelength, lifetime, and polarization. The more of these features are acquired in a single measurement, the more can be learned about the sample, i.e., the microenvironment of the fluorescence probe. Polarization-resolv ...