相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
上海西格
- 库存:
57
- 靶点:
详见说明书
- 级别:
详见说明书
- 目录编号:
详见说明书
- 克隆性:
多克隆
- 抗原来源:
Rabbit
- 保质期:
详见说明书
- 抗体英文名:
Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha
- 抗体名:
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶p38α抗体
- 标记物:
详见说明书
- 宿主:
详见说明书
- 适应物种:
详见说明书
- 免疫原:
KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human P38MAPK N-terminus
- 亚型:
IgG
- 形态:
详见说明书
- 应用范围:
WB=1:100-500 ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500
- 浓度:
1mg/1ml
- 保存条件:
详见说明书
- 规格:
0.1ml/100μg 0.2ml/200μg
抗体制备过程:
1.材料与试剂
a.提取的动物 Ig
b.弗氏完全佐剂和弗氏不完全佐剂
c.青霉素和链霉素
d.实验动物 兔
e.其它材料及试剂
2、选择实验活体。
3、进行动物免疫实验。
4、试取血样进行测试,查看免疫效果。
5、如果免疫成功,杀死实验活体,采集全部血清。
6、纯化出抗体。
7、鉴定抗体。胎牛血清(无菌采制)

英文名称 Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha
中文名称 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶p38α抗体
别 名 CSAID Binding Protein 1; CSAID binding protein; CSAID-binding protein; Csaids binding protein; CSBP 1; CSBP 2; CSBP; CSBP1; CSBP2; CSPB 1; CSPB1; Cytokine suppressive anti inflammatory drug binding protein; Cytokine suppressive anti-inflammatory drug-binding protein; EXIP; MAP kinase 14; MAP kinase MXI2; MAP kinase p38 alpha; MAPK 14; MAPK14; MAX interacting protein 2; MAX-interacting protein 2; Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase 14; Mitogen activated protein kinase p38 alpha; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 alpha; MK14_HUMAN; Mxi 2; Mxi2; p38 ALPHA; p38; p38 MAP kinase; p38 MAPK; p38/MAPK; p38 mitogen activated protein kinase; p38ALPHA; p38alpha Exip; PRKM14; PRKM15; RK; SAPK 2A; SAPK2A; Stress Activated Protein Kinase 2A.
浓 度 1mg/1ml
规 格 0.1ml/100μg 0.2ml/200μg 1ml/1mg
抗体来源 Rabbit
克隆类型 polyclonal
交叉反应 Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Rabbit
产品类型 一抗
研究领域 肿瘤 免疫学 信号转导 细胞凋亡 转录调节因子
蛋白分子量 predicted molecular weight: 41kDa
性 状 Lyophilized or Liquid
免 疫 原 KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human P38MAPK N-terminus
亚 型 IgG
纯化方法 affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 with 10 mg/ml BSA and 0.1% Sodium azide
产品应用 WB=1:100-500 ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500
产品介绍 The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is activated by various environmental stresses and proinflammatory cytokines. The activation requires its phosphorylation by MAP kinase kinases(MKKs), or its autophosphorylation triggered by the interaction of MAP3K7IP1/TAB1 protein with this kinase. The substrates of this kinase include transcription regulator ATF2, MEF2C, and MAX, cell cycle regulator CDC25B, and tumor suppressor p53, which suggest the roles of this kinase in stress related transcription and cell cycle regulation, as well as in genotoxic stress response. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.
Function : Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK14 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. Some of the targets are downstream kinases which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 can directly phosphorylate and activate transcription factors such as CREB1, ATF1, the NF-kappa-B isoform RELA/NFKB3, STAT1 and STAT3, but can also phosphorylate histone H3 and the nucleosomal protein HMGN1. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 play important roles in the rapid induction of immediate-early genes in response to stress or mitogenic stimuli, either by inducing chromatin remodeling or by recruiting the transcription machinery. On the other hand, two other kinase targets, MAPKAPK2/MK2 and MAPKAPK3/MK3, participate in the control of gene expression mostly at the post-transcriptional level, by phosphorylating ZFP36 (tristetraprolin) and ELAVL1, and by regulating EEF2K, which is important for the elongation of mRNA during translation. MKNK1/MNK1 and MKNK2/MNK2, two other kinases activated by p38 MAPKs, regulate protein synthesis by phosphorylating the initiation factor EIF4E2. MAPK14 interacts also with casein kinase II, leading to its activation through autophosphorylation and further phosphorylation of TP53/p53. In the cytoplasm, the p38 MAPK pathway is an important regulator of protein turnover. For example, CFLAR is an inhibitor of TNF-induced apoptosis whose proteasome-mediated degradation is regulated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation. In a similar way, MAPK14 phosphorylates the ubiquitin ligase SIAH2, regulating its activity towards EGLN3. MAPK14 may also inhibit the lysosomal degradation pathway of autophagy by interfering with the intracellular trafficking of the transmembrane protein ATG9. Another function of MAPK14 is to regulate the endocytosis of membrane receptors by different mechanisms that impinge on the small GTPase RAB5A. In addition, clathrin-mediated EGFR internalization induced by inflammatory cytokines and UV irradiation depends on MAPK14-mediated phosphorylation of EGFR itself as well as of RAB5A effectors. Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane proteins is regulated by p38 MAPKs as well. In response to inflammatory stimuli, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate the membrane-associated metalloprotease ADAM17. Such phosphorylation is required for ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of TGF-alpha family ligands, which results in the activation of EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Another p38 MAPK substrate is FGFR1. FGFR1 can be translocated from the extracellular space into the cytosol and nucleus of target cells, and regulates processes such as rRNA synthesis and cell growth. FGFR1 translocation requires p38 MAPK activation. In the nucleus, many transcription factors are phosphorylated and activated by p38 MAPKs in response to different stimuli. Classical examples include ATF1, ATF2, ATF6, ELK1, PTPRH, DDIT3, TP53/p53 and MEF2C and MEF2A. The p38 MAPKs are emerging as important modulators of gene expression by regulating chromatin modifiers and remodelers. The promoters of several genes involved in the inflammatory response, such as IL6, IL8 and IL12B, display a p38 MAPK-dependent enrichment of histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Ser-10' (H3S10ph) in LPS-stimulated myeloid cells. This phosphorylation enhances the accessibility of the cryptic NF-kappa-B-binding sites marking promoters for increased NF-kappa-B recruitment. Phosphorylates CDC25B and CDC25C which is required for binding to
14-3-3
proteins and leads to initiation of a G2 delay after ultraviolet radiation. Phosphorylates TIAR following DNA damage, releasing TIAR from GADD45A mRNA and preventing mRNA degradation. The p38 MAPKs may also have kinase-independent roles, which are thought to be due to the binding to targets in the absence of phosphorylation. Protein O-Glc-N-acylation catalyzed by the OGT is regulated by MAPK14, and, although OGT does not seem to be phosphorylated by MAPK14, their interaction increases upon MAPK14 activation induced by glucose deprivation. This interaction may regulate OGT activity by recruiting it to specific targets such as neurofilament H, stimulating its O-Glc-N-acylation. Required in mid-fetal development for the growth of embryo-derived blood vessels in the labyrinth layer of the placenta. Also plays an essential role in developmental and stress-induced erythropoiesis, through regulation of EPO gene expression. Isoform MXI2 activation is stimulated by mitogens and oxidative stress and only poorly phosphorylates ELK1 and ATF2. Isoform EXIP may play a role in the early onset of apoptosis. Phosphorylates S100A9 at 'Thr-113'.
Subunit : Binds to a kinase interaction motif within the protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTPRR (By similarity). This interaction retains MAPK14 in the cytoplasm and prevents nuclear accumulation. Interacts with SPAG9 and GADD45A. Interacts with CDC25B, CDC25C, DUSP1, DUSP10, DUSP16, NP60, FAM48A and TAB1. Interacts with casein kinase II subunits CSNK2A1 and CSNK2B.
Subcellular Location : Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Post-translational modifications : Dually phosphorylated on Thr-180 and Tyr-182 by the MAP2Ks MAP2K3/MKK3, MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K6/MKK6 in response to inflammatory citokines, environmental stress or growth factors, which a ctivates the enzyme. Dual phosphorylation can also be mediated by TAB1-mediated autophosphorylation. TCR engagement in T-cells also leads to Tyr-323 phosphorylation by ZAP70. Dephosphorylated and inactivated by DUPS1, DUSP10 and DUSP16.
Acetylated at Lys-53 and Lys-152 by KAT2B and EP300. Acetylation at Lys-53 increases the affinity for ATP and enhances kinase activity. Lys-53 and Lys-152 are deacetylated by HDAC3.
Ubiquitinated. Ubiquitination leads to degradation by the proteasome pathway.
Similarity : Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. MAP kinase subfamily.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Database links :
Entrez Gene: 403856 Dog
Entrez Gene: 1432 Human
Entrez Gene: 26416 Mouse
Entrez Gene: 81649 Rat
GenBank: NM_001315 Human
GenBank: NM_139012 Human
GenBank: NM_011951 Mouse
GenBank: NM_031020 Rat
Omim: 600289 Human
SwissProt: O02812 Dog
SwissProt: Q16539 Human
SwissProt: P47811 Mouse
SwissProt: P70618 Rat
Unigene: 485233 Human
Unigene: 311337 Mouse
Unigene: 88085 Rat
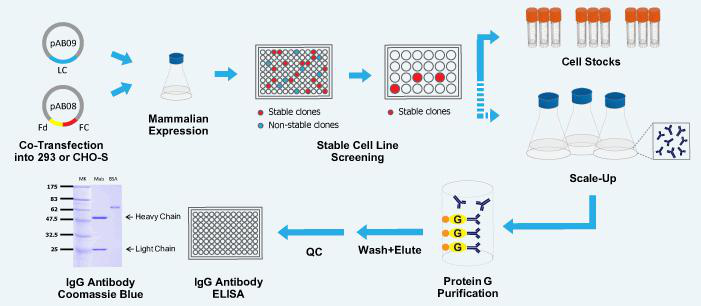
实验原理 :
(1)特异性结合抗原:抗体本身不能直接溶解或杀伤带有特异抗原的靶细胞,通常需要补体或吞噬细胞等共同发挥效应以清除病原微生物或导致病理损伤。然而,抗体可通过与病毒或毒素的特异性结合,直接发挥中和病毒的作用。
(2)活补体:IgM、IgG1、IgG2和IgG3可通过经典途径激活补体,凝聚的IgA、IgG4和IgE可通过替代途径激活补体。
(3)结合细胞:不同类别的免疫球蛋白,可结合不同种的细胞,参与免疫应答。
(4)可通过胎盘及粘膜:免疫球蛋白G(IgG)能通过胎盘进入胎儿血流中,使胎儿形成自然被动
免疫。免疫球蛋白A(IgA)可通过消化道及呼吸道粘膜,是粘膜局部抗感染免疫的主要因素。
(5)具有抗原性:抗体分子是一种蛋白质,也具有刺机体产生免疫应答的性能。不同的免疫球蛋白分子,各具有不同的抗原性。
(6)抗体对理化因子的抵抗力与一般球蛋白相同:不耐热,60~70℃即被破坏。各种酶及能使蛋白质凝固变性的物质,均能破坏抗体的作用。抗体可被中性盐类沉淀。在上常可用硫酸铵或硫酸钠从免疫血清中沉淀出含有抗体的球蛋白,再经透析法将其纯化。
我司提供以下技术外包服务:
1. Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha抗体分子生物学:质粒抽提、PCR、Q-PCR、RT-PCR、分子生物学:基因合成、引物合成、基因测序、载体构建等
2.蛋白工程:原核、哺乳动物蛋白表达系统等
3.病毒包装:腺病毒、慢病毒等
4.抗体工程:磁珠分选、病理染色、WB、ELISA、IP、IF、IHC、FACS、Confocal等等
5.细胞工程:细胞表型分析(凋亡、增殖、周期、迁移、侵袭、修复、克隆形成)、细胞培养、细胞膜制备、稳定细胞株构建、细胞RNAi技术等等。
抗体的鉴定:
1)抗体的效价鉴定:鉴定效价的方法很多,包括有试管凝集反应,琼脂扩散试验,酶联免疫吸附试验等。常用的抗原所制备的抗体一般都有约成的鉴定效价的方法,以资比较。如制备抗抗体的效价,一般就采用琼脂扩散试验来鉴定。
2)抗体的特异性鉴定:抗体的特异性是指与相应抗原或近似抗原物质的识别能力。抗体的特异性高,它的识别能力就强。衡量特异性通常以交叉反应率来表示。交叉反应率可用竞争抑制试验测定。以不同浓度抗原和近似抗原分别做竞争抑制曲线,计算各自的结合率,求出各自在IC50时的浓度,并按公式计算交叉反应率。
3)真核翻译起始因子2C2抗体的亲和力:是指抗体和抗原结合的牢固程度。亲和力的高低是由抗原分子的大小,抗体分子的结合位点与抗原决定簇之间立体构型的合适度决定的。有助于维持抗原抗体复合物稳定的分子间力有氢键,疏水键,侧链相反电荷基因的库仑力,范德华力和空间斥力。亲和力常以亲和常数K表示,K的单位是L/mol。
Anti-Rb/RB1 protein/FITC 荧光素标记视网膜母细胞瘤相关蛋白1抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG Whole serum 兔抗羊IgG抗血清Multi-class antibodies规格: 1ml
胰岛素样生长因子-II抗体 Anti-IGF-II 0.1ml
Mouse Anti-Bov IgG 小鼠抗IgG 1mg
FXYD6 英文名称: FXYD离子转运调节因子6抗体 0.2ml
Rhesus antibody Rh phospho-Pyk2/PTK2B(Tyr402) 0酸化富含脯氨酸的酪氨酸激酶2抗体 规格 0.1ml
Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG Whole serum 兔抗羊IgG抗血清Multi-class antibodies规格: 1ml
Anti-phospho-SHC (Tyr349) /FITC 荧光素标记0酸化SH2结构域转化蛋白1抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Apaf-1 (Apoptosis protease activating factor-1)(NT) 凋亡蛋白活性因子-1(抗原)Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.5mg
中分子量神经丝蛋白抗体 Anti-NF-M 0.1ml
Stra8 英文名称: 视黄酸激活基因8抗体 0.1ml
ELK1 英文名称: 细胞转录因子ELK1抗体 0.1ml
Rhesus antibody Rh Phospho-p90RSK (Thr573) 0酸化丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶p90RSK蛋白抗体 规格 0.1ml
Apaf-1 (Apoptosis protease activating factor-1)(NT) 凋亡蛋白活性因子-1(抗原)Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.5mg
mouse IFN- Alpha 小鼠α-干扰素Multi-class antibodies规格: 48T
Anti-ERK1/MAPK3 原活化蛋白激酶3抗体Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.1ml
Rhesus antibody Rh MTCH1 细胞增殖诱导蛋白60(早老素相关蛋白) 规格 0.2ml
HNP1-3(Human neutrophil peptide 1-3) ELISA Kit 人中性粒细胞防御素1-3 96T
SMCP 英文名称: 线粒体相关富含半胱酸蛋白抗体 0.1ml
CD24 英文名称: CD24抗体 0.1ml
Anti-ERK1/MAPK3 原活化蛋白激酶3抗体Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.1ml
鹅甾体合成急性调节蛋白(StAR)ELISA试剂盒 96T/48T 试剂盒 组装/原装
人牙骨质蛋白1(CEMP-1)免疫试剂盒 Human Cemeum Protein 1,CEMP-1 ELISA Kit
人抗酿酒酵母抗体(ASCA)ELISA试剂盒 ,英文名: ASCA ELISA Kit
Rathepaticlipase,HLELISA试剂盒大鼠肝脂酶(HL)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
HumanFibrinogen,FbgELISA试剂盒人血纤蛋白原(Fbg)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
Humaninducibleniicoxidesyhase,iNOSELISAKit人诱导型合成酶(iNOS)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha抗体人Ⅰ型前胶原C末端肽(CⅠCP)ELISA 试剂盒 96T/48T 试剂盒 组装/原装
兔阿霉素(ADR)免疫试剂盒 Rabbit adramycin,ADR ELISA Kit
凝血因子Ⅸ(FⅨ)ELISA试剂盒 ,英文名: FⅨ ELISA Kit
RabbitOsteoprotegerin,OPGELISA试剂盒兔骨保护素(OPG)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
HumanArginase,ArgELISA试剂盒人精氨酸酶(Arg)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
HumanComplemefragme3brccptor,C3bRELISAKit人补体片段3b受体(C3bR)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
1.材料与试剂
a.提取的动物 Ig
b.弗氏完全佐剂和弗氏不完全佐剂
c.青霉素和链霉素
d.实验动物 兔
e.其它材料及试剂
2、选择实验活体。
3、进行动物免疫实验。
4、试取血样进行测试,查看免疫效果。
5、如果免疫成功,杀死实验活体,采集全部血清。
6、纯化出抗体。
7、鉴定抗体。胎牛血清(无菌采制)
| 产品名称 | 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶p38α抗体 |
| 英文名称 | Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha抗体 |
| 货号 | XGK0984 |

英文名称 Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha
中文名称 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶p38α抗体
别 名 CSAID Binding Protein 1; CSAID binding protein; CSAID-binding protein; Csaids binding protein; CSBP 1; CSBP 2; CSBP; CSBP1; CSBP2; CSPB 1; CSPB1; Cytokine suppressive anti inflammatory drug binding protein; Cytokine suppressive anti-inflammatory drug-binding protein; EXIP; MAP kinase 14; MAP kinase MXI2; MAP kinase p38 alpha; MAPK 14; MAPK14; MAX interacting protein 2; MAX-interacting protein 2; Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase 14; Mitogen activated protein kinase p38 alpha; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14; Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 alpha; MK14_HUMAN; Mxi 2; Mxi2; p38 ALPHA; p38; p38 MAP kinase; p38 MAPK; p38/MAPK; p38 mitogen activated protein kinase; p38ALPHA; p38alpha Exip; PRKM14; PRKM15; RK; SAPK 2A; SAPK2A; Stress Activated Protein Kinase 2A.
浓 度 1mg/1ml
规 格 0.1ml/100μg 0.2ml/200μg 1ml/1mg
抗体来源 Rabbit
克隆类型 polyclonal
交叉反应 Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Rabbit
产品类型 一抗
研究领域 肿瘤 免疫学 信号转导 细胞凋亡 转录调节因子
蛋白分子量 predicted molecular weight: 41kDa
性 状 Lyophilized or Liquid
免 疫 原 KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human P38MAPK N-terminus
亚 型 IgG
纯化方法 affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 with 10 mg/ml BSA and 0.1% Sodium azide
产品应用 WB=1:100-500 ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500
产品介绍 The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is activated by various environmental stresses and proinflammatory cytokines. The activation requires its phosphorylation by MAP kinase kinases(MKKs), or its autophosphorylation triggered by the interaction of MAP3K7IP1/TAB1 protein with this kinase. The substrates of this kinase include transcription regulator ATF2, MEF2C, and MAX, cell cycle regulator CDC25B, and tumor suppressor p53, which suggest the roles of this kinase in stress related transcription and cell cycle regulation, as well as in genotoxic stress response. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.
Function : Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK14 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. Some of the targets are downstream kinases which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 can directly phosphorylate and activate transcription factors such as CREB1, ATF1, the NF-kappa-B isoform RELA/NFKB3, STAT1 and STAT3, but can also phosphorylate histone H3 and the nucleosomal protein HMGN1. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 play important roles in the rapid induction of immediate-early genes in response to stress or mitogenic stimuli, either by inducing chromatin remodeling or by recruiting the transcription machinery. On the other hand, two other kinase targets, MAPKAPK2/MK2 and MAPKAPK3/MK3, participate in the control of gene expression mostly at the post-transcriptional level, by phosphorylating ZFP36 (tristetraprolin) and ELAVL1, and by regulating EEF2K, which is important for the elongation of mRNA during translation. MKNK1/MNK1 and MKNK2/MNK2, two other kinases activated by p38 MAPKs, regulate protein synthesis by phosphorylating the initiation factor EIF4E2. MAPK14 interacts also with casein kinase II, leading to its activation through autophosphorylation and further phosphorylation of TP53/p53. In the cytoplasm, the p38 MAPK pathway is an important regulator of protein turnover. For example, CFLAR is an inhibitor of TNF-induced apoptosis whose proteasome-mediated degradation is regulated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation. In a similar way, MAPK14 phosphorylates the ubiquitin ligase SIAH2, regulating its activity towards EGLN3. MAPK14 may also inhibit the lysosomal degradation pathway of autophagy by interfering with the intracellular trafficking of the transmembrane protein ATG9. Another function of MAPK14 is to regulate the endocytosis of membrane receptors by different mechanisms that impinge on the small GTPase RAB5A. In addition, clathrin-mediated EGFR internalization induced by inflammatory cytokines and UV irradiation depends on MAPK14-mediated phosphorylation of EGFR itself as well as of RAB5A effectors. Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane proteins is regulated by p38 MAPKs as well. In response to inflammatory stimuli, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate the membrane-associated metalloprotease ADAM17. Such phosphorylation is required for ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of TGF-alpha family ligands, which results in the activation of EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Another p38 MAPK substrate is FGFR1. FGFR1 can be translocated from the extracellular space into the cytosol and nucleus of target cells, and regulates processes such as rRNA synthesis and cell growth. FGFR1 translocation requires p38 MAPK activation. In the nucleus, many transcription factors are phosphorylated and activated by p38 MAPKs in response to different stimuli. Classical examples include ATF1, ATF2, ATF6, ELK1, PTPRH, DDIT3, TP53/p53 and MEF2C and MEF2A. The p38 MAPKs are emerging as important modulators of gene expression by regulating chromatin modifiers and remodelers. The promoters of several genes involved in the inflammatory response, such as IL6, IL8 and IL12B, display a p38 MAPK-dependent enrichment of histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Ser-10' (H3S10ph) in LPS-stimulated myeloid cells. This phosphorylation enhances the accessibility of the cryptic NF-kappa-B-binding sites marking promoters for increased NF-kappa-B recruitment. Phosphorylates CDC25B and CDC25C which is required for binding to
Subunit : Binds to a kinase interaction motif within the protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTPRR (By similarity). This interaction retains MAPK14 in the cytoplasm and prevents nuclear accumulation. Interacts with SPAG9 and GADD45A. Interacts with CDC25B, CDC25C, DUSP1, DUSP10, DUSP16, NP60, FAM48A and TAB1. Interacts with casein kinase II subunits CSNK2A1 and CSNK2B.
Subcellular Location : Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
Post-translational modifications : Dually phosphorylated on Thr-180 and Tyr-182 by the MAP2Ks MAP2K3/MKK3, MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K6/MKK6 in response to inflammatory citokines, environmental stress or growth factors, which a ctivates the enzyme. Dual phosphorylation can also be mediated by TAB1-mediated autophosphorylation. TCR engagement in T-cells also leads to Tyr-323 phosphorylation by ZAP70. Dephosphorylated and inactivated by DUPS1, DUSP10 and DUSP16.
Acetylated at Lys-53 and Lys-152 by KAT2B and EP300. Acetylation at Lys-53 increases the affinity for ATP and enhances kinase activity. Lys-53 and Lys-152 are deacetylated by HDAC3.
Ubiquitinated. Ubiquitination leads to degradation by the proteasome pathway.
Similarity : Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. MAP kinase subfamily.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Database links :
Entrez Gene: 403856 Dog
Entrez Gene: 1432 Human
Entrez Gene: 26416 Mouse
Entrez Gene: 81649 Rat
GenBank: NM_001315 Human
GenBank: NM_139012 Human
GenBank: NM_011951 Mouse
GenBank: NM_031020 Rat
Omim: 600289 Human
SwissProt: O02812 Dog
SwissProt: Q16539 Human
SwissProt: P47811 Mouse
SwissProt: P70618 Rat
Unigene: 485233 Human
Unigene: 311337 Mouse
Unigene: 88085 Rat

实验原理 :
(1)特异性结合抗原:抗体本身不能直接溶解或杀伤带有特异抗原的靶细胞,通常需要补体或吞噬细胞等共同发挥效应以清除病原微生物或导致病理损伤。然而,抗体可通过与病毒或毒素的特异性结合,直接发挥中和病毒的作用。
(2)活补体:IgM、IgG1、IgG2和IgG3可通过经典途径激活补体,凝聚的IgA、IgG4和IgE可通过替代途径激活补体。
(3)结合细胞:不同类别的免疫球蛋白,可结合不同种的细胞,参与免疫应答。
(4)可通过胎盘及粘膜:免疫球蛋白G(IgG)能通过胎盘进入胎儿血流中,使胎儿形成自然被动
免疫。免疫球蛋白A(IgA)可通过消化道及呼吸道粘膜,是粘膜局部抗感染免疫的主要因素。
(5)具有抗原性:抗体分子是一种蛋白质,也具有刺机体产生免疫应答的性能。不同的免疫球蛋白分子,各具有不同的抗原性。
(6)抗体对理化因子的抵抗力与一般球蛋白相同:不耐热,60~70℃即被破坏。各种酶及能使蛋白质凝固变性的物质,均能破坏抗体的作用。抗体可被中性盐类沉淀。在上常可用硫酸铵或硫酸钠从免疫血清中沉淀出含有抗体的球蛋白,再经透析法将其纯化。
我司提供以下技术外包服务:
1. Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha抗体分子生物学:质粒抽提、PCR、Q-PCR、RT-PCR、分子生物学:基因合成、引物合成、基因测序、载体构建等
2.蛋白工程:原核、哺乳动物蛋白表达系统等
3.病毒包装:腺病毒、慢病毒等
4.抗体工程:磁珠分选、病理染色、WB、ELISA、IP、IF、IHC、FACS、Confocal等等
5.细胞工程:细胞表型分析(凋亡、增殖、周期、迁移、侵袭、修复、克隆形成)、细胞培养、细胞膜制备、稳定细胞株构建、细胞RNAi技术等等。
抗体的鉴定:
1)抗体的效价鉴定:鉴定效价的方法很多,包括有试管凝集反应,琼脂扩散试验,酶联免疫吸附试验等。常用的抗原所制备的抗体一般都有约成的鉴定效价的方法,以资比较。如制备抗抗体的效价,一般就采用琼脂扩散试验来鉴定。
2)抗体的特异性鉴定:抗体的特异性是指与相应抗原或近似抗原物质的识别能力。抗体的特异性高,它的识别能力就强。衡量特异性通常以交叉反应率来表示。交叉反应率可用竞争抑制试验测定。以不同浓度抗原和近似抗原分别做竞争抑制曲线,计算各自的结合率,求出各自在IC50时的浓度,并按公式计算交叉反应率。
3)真核翻译起始因子2C2抗体的亲和力:是指抗体和抗原结合的牢固程度。亲和力的高低是由抗原分子的大小,抗体分子的结合位点与抗原决定簇之间立体构型的合适度决定的。有助于维持抗原抗体复合物稳定的分子间力有氢键,疏水键,侧链相反电荷基因的库仑力,范德华力和空间斥力。亲和力常以亲和常数K表示,K的单位是L/mol。
Anti-Rb/RB1 protein/FITC 荧光素标记视网膜母细胞瘤相关蛋白1抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG Whole serum 兔抗羊IgG抗血清Multi-class antibodies规格: 1ml
胰岛素样生长因子-II抗体 Anti-IGF-II 0.1ml
Mouse Anti-Bov IgG 小鼠抗IgG 1mg
FXYD6 英文名称: FXYD离子转运调节因子6抗体 0.2ml
Rhesus antibody Rh phospho-Pyk2/PTK2B(Tyr402) 0酸化富含脯氨酸的酪氨酸激酶2抗体 规格 0.1ml
Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG Whole serum 兔抗羊IgG抗血清Multi-class antibodies规格: 1ml
Anti-phospho-SHC (Tyr349) /FITC 荧光素标记0酸化SH2结构域转化蛋白1抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Apaf-1 (Apoptosis protease activating factor-1)(NT) 凋亡蛋白活性因子-1(抗原)Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.5mg
中分子量神经丝蛋白抗体 Anti-NF-M 0.1ml
Stra8 英文名称: 视黄酸激活基因8抗体 0.1ml
ELK1 英文名称: 细胞转录因子ELK1抗体 0.1ml
Rhesus antibody Rh Phospho-p90RSK (Thr573) 0酸化丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶p90RSK蛋白抗体 规格 0.1ml
Apaf-1 (Apoptosis protease activating factor-1)(NT) 凋亡蛋白活性因子-1(抗原)Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.5mg
mouse IFN- Alpha 小鼠α-干扰素Multi-class antibodies规格: 48T
Anti-ERK1/MAPK3 原活化蛋白激酶3抗体Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.1ml
Rhesus antibody Rh MTCH1 细胞增殖诱导蛋白60(早老素相关蛋白) 规格 0.2ml
HNP1-3(Human neutrophil peptide 1-3) ELISA Kit 人中性粒细胞防御素1-3 96T
SMCP 英文名称: 线粒体相关富含半胱酸蛋白抗体 0.1ml
CD24 英文名称: CD24抗体 0.1ml
Anti-ERK1/MAPK3 原活化蛋白激酶3抗体Multi-class antibodies规格: 0.1ml
鹅甾体合成急性调节蛋白(StAR)ELISA试剂盒 96T/48T 试剂盒 组装/原装
人牙骨质蛋白1(CEMP-1)免疫试剂盒 Human Cemeum Protein 1,CEMP-1 ELISA Kit
人抗酿酒酵母抗体(ASCA)ELISA试剂盒 ,英文名: ASCA ELISA Kit
Rathepaticlipase,HLELISA试剂盒大鼠肝脂酶(HL)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
HumanFibrinogen,FbgELISA试剂盒人血纤蛋白原(Fbg)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
Humaninducibleniicoxidesyhase,iNOSELISAKit人诱导型合成酶(iNOS)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha抗体人Ⅰ型前胶原C末端肽(CⅠCP)ELISA 试剂盒 96T/48T 试剂盒 组装/原装
兔阿霉素(ADR)免疫试剂盒 Rabbit adramycin,ADR ELISA Kit
凝血因子Ⅸ(FⅨ)ELISA试剂盒 ,英文名: FⅨ ELISA Kit
RabbitOsteoprotegerin,OPGELISA试剂盒兔骨保护素(OPG)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
HumanArginase,ArgELISA试剂盒人精氨酸酶(Arg)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
HumanComplemefragme3brccptor,C3bRELISAKit人补体片段3b受体(C3bR)ELISA试剂盒规格:96T/48T
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料
Anti-p38MAPK/MAPK14/p38Alpha抗体
询价