相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
江西江蓝纯生物试剂有限公司
- 库存:
98
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
Hemoglobin alpha
- 抗体名:
血红蛋白α/Hemoglobin A1c抗体
- 适应物种:
人/动物/植物
- 应用范围:
WB,ELISA等
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
-20 °
- 规格:
100ul/200ul
| 规格: | 100ul | 产品价格: | ¥1580.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 规格: | 200ul | 产品价格: | ¥2480.0 |
英文名称 : Hemoglobin alpha
中文名称 : 血红蛋白α/Hemoglobin A1c抗体
别 名 : Hemoglobin A1c; Alpha globin; Hba1; HBA2; HBAM; Hemoglobin alpha 1; Hemoglobin alpha adult chain 1; HBA_HUMAN.
研究领域 : 心血管 细胞生物 糖尿病 内分泌病 糖蛋白
抗体来源 : Rabbit
克隆类型 : Polyclonal
交叉反应 : Human,
产品应用 : ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 IF=1:50-200 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
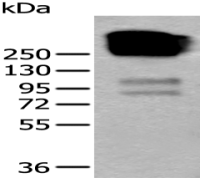
分 子 量 : 15kDa
细胞定位 : 细胞浆 细胞外基质 分泌型蛋白
性 状 : Lyophilized or Liquid
浓 度 : 1mg/ml
免 疫 原 : KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Hemoglobin alpha:1-100/142
亚 型 : IgG
纯化方法 : affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 : 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件 : Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMed : PubMed
产品介绍 : The human alpha globin gene cluster located on chromosome 16 spans about 30 kb and includes seven loci: 5'- zeta - pseudozeta - mu - pseudoalpha-1 - alpha-2 - alpha-1 - theta - 3'. The alpha-2 (HBA2) and alpha-1 (HBA1) coding sequences are identical. These genes differ slightly over the 5' untranslated regions and the introns, but they differ significantly over the 3' untranslated regions. Two alpha chains plus two beta chains constitute HbA, which in normal adult life comprises about 97% of the total hemoglobin; alpha chains combine with delta chains to constitute HbA-2, which with HbF (fetal hemoglobin) makes up the remaining 3% of adult hemoglobin. Alpha thalassemias result from deletions of each of the alpha genes as well as deletions of both HBA2 and HBA1; some nondeletion alpha thalassemias have also been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
Function:
Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues.
Subunit:
Heterotetramer of two alpha chains and two beta chains in adult hemoglobin A (HbA); two alpha chains and two delta chains in adult hemoglobin A2 (HbA2); two alpha chains and two epsilon chains in early embryonic hemoglobin Gower-2; two alpha chains and two gamma chains in fetal hemoglobin F (HbF).
Subcellular Location:
hemoglobin complex.
Tissue Specificity:
Red blood cells.
Post-translational modifications:
The initiator Met is not cleaved in variant Thionville and is acetylated.
DISEASE:
Defects in HBA1 may be a cause of Heinz body anemias (HEIBAN) [MIM:140700]. This is a form of non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia of Dacie type 1. After splenectomy, which has little benefit, basophilic inclusions called Heinz bodies are demonstrable in the erythrocytes. Before splenectomy, diffuse or punctate basophilia may be evident. Most of these cases are probably instances of hemoglobinopathy. The hemoglobin demonstrates heat lability. Heinz bodies are observed also with the Ivemark syndrome (asplenia with cardiovascular anomalies) and with glutathione peroxidase deficiency.
Defects in HBA1 are the cause of alpha-thalassemia (A-THAL) [MIM:604131]. The thalassemias are the most common monogenic diseases and occur mostly in Mediterranean and Southeast Asian populations. The hallmark of alpha-thalassemia is an imbalance in globin-chain production in the adult HbA molecule. The level of alpha chain production can range from none to very nearly normal levels. Deletion of both copies of each of the two alpha-globin genes causes alpha(0)-thalassemia, also known as homozygous alpha thalassemia. Due to the complete absence of alpha chains, the predominant fetal hemoglobin is a tetramer of gamma-chains (Bart hemoglobin) that has essentially no oxygen carrying capacity. This causes oxygen starvation in the fetal tissues leading to prenatal lethality or early neonatal death. The loss of three alpha genes results in high levels of a tetramer of four beta chains (hemoglobin H), causing a severe and life-threatening anemia known as hemoglobin H disease. Untreated, most patients die in childhood or early adolescence. The loss of two alpha genes results in mild alpha-thalassemia, also known as heterozygous alpha-thalassemia. Affected individuals have small red cells and a mild anemia (microcytosis). If three of the four alpha-globin genes are functional, individuals are completely asymptomatic. Some rare forms of alpha-thalassemia are due to point mutations (non-deletional alpha-thalassemia). The thalassemic phenotype is due to unstable globin alpha chains that are rapidly catabolized prior to formation of the alpha-beta heterotetramers.
Note=Alpha(0)-thalassemia is associated with non-immune hydrops fetalis, a generalized edema of the fetus with fluid accumulation in the body cavities due to non-immune causes. Non-immune hydrops fetalis is not a diagnosis in itself but a symptom, a feature of many genetic disorders, and the end-stage of a wide variety of disorders.
Defects in HBA1 are the cause of hemoglobin H disease (HBH) [MIM:613978]. HBH is a form of alpha-thalassemia due to the loss of three alpha genes. This results in high levels of a tetramer of four beta chains (hemoglobin H), causing a severe and life-threatening anemia. Untreated, most patients die in childhood or early adolescence.
Similarity:
Belongs to the globin family.
SWISS:
P69905
Gene ID:
3039
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
产品图片

风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验抗体的结构决定了其对应的功能,同一抗体的V区和C区的氨基酸组成和顺序不同,决定了其功能上的差异。V区和C区的组成和结构,决定了抗体的生物学功能。 图1:抗体的主要功能(图片来源:Abbas et al: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7e.) 1、特异性识别功能 抗体可以通过其结构上的可变区域与抗原结合,同时,具有极高的特异性。这种特异性识别功能可以使抗体识别和结合到感染的病原体,肿瘤细胞等不同种类的分子,帮助免疫系统识别并定位到这些分子,进而启动
在生命科学和医学基础研究中,或多或少都需要用到抗体。抗体的应用场景不同、标记物众多,且针对同一标记物市场上往往有多个抗体可供选择,那么,我们如何从成百万上千万种抗体中,挑选出我们想要的那支呢? 在我们6月份的关于抗体的调研活动中,我们发现,大家更多的是去参考文献或专利中的材料和方法部分,这无疑很大程度上保证了抗体的有效性。其次有45%和34%的受访者会用到百度和谷歌,然而这两个搜索引擎覆盖面颇广,经常会出现抗体无关的搜索结果,而专业用于查找抗体的网站,大家却知之甚少。 因此,本次文章中
脾细胞与小鼠骨髓瘤细胞(P3-X63/Ag8)融合,融合的细胞既获得了亲代脾细胞分泌特异性抗体的特性,又具有骨髓瘤细胞大量繁殖的能力,成为一种既能分泌特异性抗体又能长命的杂交瘤细胞。该技术为抗体的分子生物学研究提供了全新的手段。极大地促进了免疫学,遗传学,分子生物学的快速发展。 但传统抗体目前也面临诸多问题,如: 每使用一管新抗体都需要进行滴定测试; 多种同型对照,实验设计繁琐; 需要添加Fc阻断试剂; 抗体不佳,阳性细胞群不明显; 抗体作为细胞生物学和生物化学中最重要的试剂之一,科学界每年在这类
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料